
The Project Gutenberg EBook of Jersey City and its Historic Sites, by Harriet Phillips Eaton This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license Title: Jersey City and its Historic Sites Author: Harriet Phillips Eaton Release Date: January 10, 2015 [EBook #47936] Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK JERSEY CITY AND ITS HISTORIC SITES *** Produced by Alan and the Online Distributed Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from images generously made available by The Internet Archive)

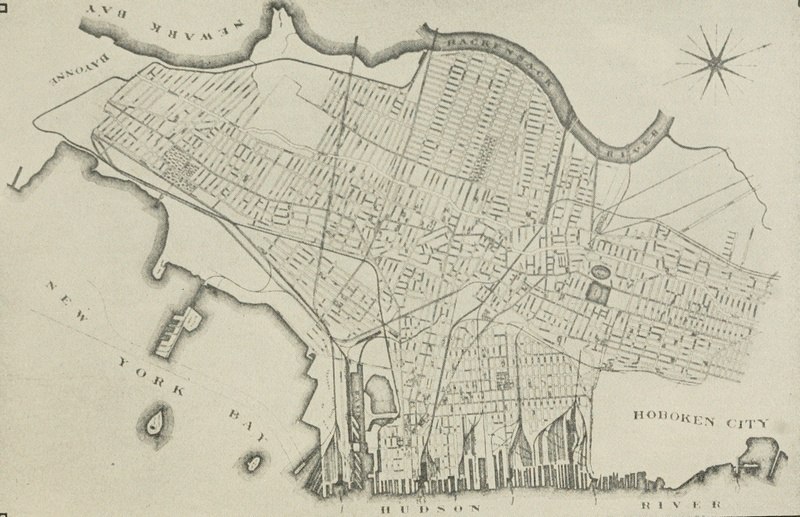
Map of Jersey City, N.J.
"Perhaps a remembrance of these things will prove a source of future pleasure".
"These who have insured their remembrance by their deserts."—Virgil.
CONTENTS
From the Minutes of the Literature Committee of the Woman's Club of Jersey City.
At a meeting of the Committee January 5th, 1898, one of the subjects for the day was "Jersey City's Old Landmarks." In the discussion that followed, Miss M. Louise Edge moved that Mrs. Eaton be requested to write a short history of Jersey City, to be published by the Club: the proceeds of which to be used to erect memorial tablets on historic sites of the Colonial and Revolutionary periods.
At the meeting of October 12th, 1898, Mrs. Eaton made the following report:
Madam Chairman and Ladies of the Literature Committee:
I take pleasure in reporting that in accordance with the request of this Committee embodied in the motion made by Miss M. Louise Edge upon January 5th, 1898, I have prepared the story of Jersey City. My authorities have been: Winfield's History of Hudson County, The Jersey City Journal's History of Jersey City, Colonial and City Records, Versteeg's Translation of[Pg 8] the Deacons Accounts of the Bergen Church, Taylor's Annals of the Classis and Township of Bergen, and numerous descendants of the old colonial families,—the Van Reypens, Van Horns, Van Winkles, Sips, Newkirks and many others, to all of whom I am greatly indebted. Also to Dr. Brett, who has kindly assisted me with his great store of historic data.
I wish particularly to express my great indebtedness to Mr. C. C. Van Reypen, who, with his wonderful memory and knowledge of Bergen, has been of invaluable assistance to me.
Respectfully submitted,
Harriet Phillip Eaton
Before the white race came to America, the locality now known as Jersey City, was occupied by a branch of the Minsi division of the Lenni Lenape Nation of the Red Men, and was called Sheyichbi. The whole of the present state of New Jersey belonged to the Lenape, and was occupied by bands bearing different names according to the special features of the locality, but all recognizing their unity as one people. Those who lived here, along the western shore of the New York Bay, extending to the sea, were known as the Wapings, or Pomptons, and were the first of the Lenape to meet the white man when Verrazano visited this harbor in 1524. Their last home was along the Raritan river. The name Lenni Lenape means "Men of our Nation," and they claimed to be the oldest nation and root of the great Algonkin stock, which, in its various divisions, with forty distinct dialects, occupied this continent from Hudson's Bay to South Carolina, and from the Atlantic to the Mississippi and the great plains, with the exception of a portion east of the Lakes where the Huron Iroquois dwelt. The other Algonkin nations were spoken of by them as "children," "Grandchildren," or "younger brothers," and to them was always accorded the respectful title of "grandfathers." Their traditions taught them that they came from[Pg 10] Shinaki, the "Land of the Fir Trees," which was probably north of Lake Superior, and in their migrations they came upon the Cherokees, probably in the ninth or tenth century of our era, with whom they fought one hundred years for possession of the Ohio Valley. Finally the Cherokees went south and the Lenape eventually, in the eleventh or twelfth century, made their home in the mountainous region of the head waters of the Delaware river. Their hunting grounds included lands now in Pennsylvania, New York and New Jersey. In 1758, New Jersey paid them $5,000 for their lands in this State.
They were called by the western nations Wapenachki,—"People of the Rising of the Sun." The name Delaware was given to them and one of their rivers, after Lord de la Ware, which they at first resented but accepted it after being told that he was a great "Brave." In character they were a noble spirited but gentle, kindly people, and all the early writers concur in testimony to their hospitality. Each family lived in its separate wigwam, a wattled hut with rounded top, thatched with mats woven of corn leaves, sweet flag, or bark of trees. These were built in groups and usually surrounded with palisades of small tree trunks firmly planted in the ground, sometimes two or three rows, interlaced, and from twenty to thirty feet in height. Their clothing was made of deer skin, soft and pliable and beautifully embroidered with wampum beads or dyed porcupine quills. In some of the arts they had attained great skill, excelling in dressing deer skins and in feather work; carved stone, made ornaments of shell and a rude pottery, some in the shape of animals. [Pg 11]They recognized the value of the Trenton clays and Indian potters used them for centuries before the white men came. While their weapons and utensils were principally of stone, they also used copper, both native New Jersey ore and that brought from Lake Superior, which they deftly hammered into shape. Old mining holes and Indian tools have been found between Elizabethtown and New York. Bowls were carved from wood and from soap-stone, kettles were made of the latter which would hold from ten to twelve gallons. They used both vegetable and mineral paints and dyes; were very expert fishermen and hunters.
They were accurate in computing time and had some astronomical knowledge; women and children could give names to many of the stars, and their year began with the first moon after the February moon. The time for planting was calculated by the rising of Taurus in a certain quarter. To this constellation they gave the name of a mythical great horned beast. They had a word for year, and counted their ages and sequence of events by yearly periods, but recognized only twelve moons in the year. They kept a record of the years by adding a black bead of wampum for each year in a belt kept for the purpose. Their picture writing was scratched on stones or cut or painted on bark or wood. It was a record of current events, the past history of the nation, and in memory of famous men, events, and actions of note. They also recorded abstract ideas, as, when an Indian gave William Penn a drawing of the "Great Man" within a series of concentric circles as their idea of God. These picture writings were understood and could be read by the various branches of the[Pg 12] Algonkin stock. Bunches of slender sticks notched or painted were also used as records.
In religion, they worshipped Light and its representatives, the Sun, Fire—"a special messenger to the Sun," the Four Winds—"Bringers of rain and sunshine," and Totemic Animals. "Light was the body or fountain of Deity," something "All Light, a Being in whom the earth and all things in it may be seen; a Great Man clothed with the day, yea, with the brightest day, a day of many years, yea, a day of everlasting continuance. From Him proceeded, in Him were, to Him returned all things, and the souls of all things." This was their faith taught by their Priests, called "Powow," meaning dreamer. They interpreted dreams and claimed to have visions which foretold future events. They believed in reincarnation and that the pure in heart might recall former lives. There were traces of the survival of Serpent worship among the people of this locality. Cast-off serpent skins were believed to have wonderful curative properties and supplications were offered to them. In 1683 Penn said there were ten divisions of the Lenape, numbering about six thousand souls, but they soon began to decrease from disease, massacres and migrations. The New Jersey Indians rapidly died out, Peter Kalm said,—"Smallpox had destroyed increditable numbers, but brandy had killed most of the Indians."
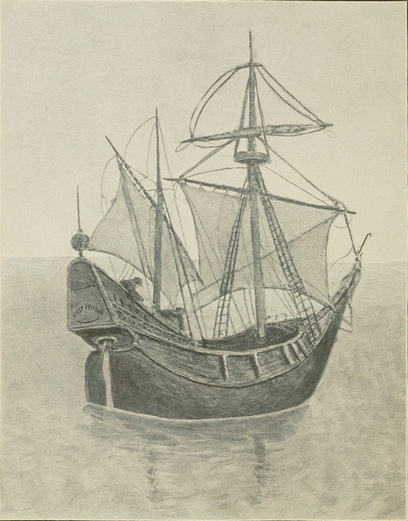

Hudson's Half Moon.
In the fall of 1609, Hendrik Hudson anchored the "Half Moon" off Communipaw, and the simple natives met him and said "Behold the Gods have come to visit us." Little they dreamed of the long sequence of evil results which would follow his coming and the introduction he gave them to "rum," the most potent destroyer of their race. When Hendrik Hudson anchored off Communipaw, where lower Jersey City now stands, it was largely salt marsh, and the heights above were crowned with heavy forests.
When he first came within Sandy Hook and gained his first view of Jersey shores he pronounced it a "very good land to fall in with, and a pleasant land to see." Later the country about Communipaw he thought "as pleasant a land as one need tread upon." He found an Indian village near the shore called Gemoenepa and another at Hackensack. It is said that Summit Avenue follows a part of the trail or path connecting the two villages. Hudson found the natives along the west shore, from Sandy Hook to Weehawken, friendly and generous; they brought him oysters, corn and fruits. Of the beauty of these people Verrezano, who visited New York Bay in 1524, was quite enthusiastic and declares of two chiefs that "they were more beautiful in form and feature than can possibly be described." He said that "the women greatly resemble the Antique, of the same form and beauty, very graceful, of fine countenance and pleasing appearance in manners and[Pg 14] modesty." The early writers all unite in describing these people as "generous, giving away whatever they had," also as "being sumptuously clothed in embroidered deer skins wrought in damask figures," and that the women wore more ornamental clothing than the men.
Van Der Donck says that the "wampum with which a woman's skirt was embroidered was frequently worth from one to three hundred guilders." They wore, also, wampum embroidered caps and head bands, the latter worn across the forehead and tied behind in a "beau's knot." Many earrings and curiously wrought necklaces and bracelets, with various colored feathers in their hair were worn by both men and women. Wampum and "seawant" as it was also called, were the Indian terms for beads made from clam shells. By the primitive methods of the Indians the beads were difficult to make, being ground down on grooved stones, and pierced by a sharp splinter of flint fastened in one end of a reed, the other end being slowly revolved upon the right thigh while the bead to be pierced was held between the thumb and forefinger of the left hand. The beads were usually from 1/8 to 1/4 of an inch in length, and because of the difficulty of manufacture they became one of the most valuable Indian possessions and to a certain extent a standard of value. Long Island, called by the Indians Sewan-hackey—land of shells—which was inhabited by branches of the Lenni Lenape family was the great center of wampum manufacture. There were specialists who devoted their time to making wampum. It was largely used by all of the eastern Indians, not alone for embroidery and ornamentation, but in record belts which were used in[Pg 15] their treaties. The two colors, white and purple, being wrought into figures which were mnemonic and enabled the "wampum keepers" to remember the words of the speech which were "talked into" the belt presented at the time. It was used in bunches of strings, strung in a certain manner, to represent the hereditary Chieftain name, and from the convenience of carrying it, it had become nearer to being a recognized currency than anything else of value among the Indians. Therefore it was used among the white colonists all along the coast, not only for the Indian trade but among themselves until late in the 18th century. They gave it a corresponding value to their own currency. At one time four black and eight white beads equalled a stiver, but in 1673 the Governor and Council of New Jersey decreed that henceforth three purple and six white wampum beads should equal one stiver or an English penny; twenty stivers, a guilder. As currency it was usually carried in strings, one hundred and fifty in a string, a "fathom of wampum" is often mentioned by early writers, and it was also used loose. The following list will show the value in "seewan" of the kinds of money mostly received by the Deacons of Bergen:
| st. | ||
|---|---|---|
| A piece of eight was worth | ƒ12.00 | in seewan |
| A realtje, about | 1.10 | " |
| A loan dollar | 11.00 | " |
| An £ English | 40.00 | " |
| so that $1 American was worth | 8.00 | " |
The Dutch early manufactured wampum at Hackensack, turning it upon a lathe; this manufacture was continued until late in this century.
During the French and English war the Delawares joined the French. In 1776 they joined the Federal cause and fought with us in the Revolutionary war. In their relations with Penn's colonists "they showed" to quote Dr. Brinton, "a sense of honor and regard for pledges equal at least to that of the white race." From 1782 to 1795 there was a bitter war between the white people and the Lenape owing to the desire of the whites to possess the Indian lands, which resulted in three cruel massacres of Christian Indians, and of the removal of the Lenape, first to Ohio, next to Kansas, and last to the Indian Territory. "In this long contest," as Dr. Brinton says, "the history of the relations of the white race with the Lenape is not one calculated to reflect glory upon the superior civilization and Christianity of the white race." In the war of 1863-65, one-half of the adult population of the Lenape officered by their own men were in the volunteer service of the United States. "No State in the Union furnished so many men for our armies from the same ratio of population as did the Lenape nation." The old men, women and children worked the farms and while the men were away fighting for the Union their white neighbors stole from them $20,000 worth of stock.
Of our Indian predecessors in this region the only trace remaining is in a few corrupted names of localities:
Hackensack, from Ackensack—low land.
Secaucus, from Siskakes or Sikakes—the place where the snake hides. The Indian name for Snake [Pg 17]Hill, now transferred to the upland between Pinhorne Creek and Hackensack river.
Weehawken, from Awiehaken—at the end of (the Palisades.)
Hoboken, from Hopoghan Hackingh—the land of the tobacco pipe. At this point they procured the stone from which they carved their pipes. It was a piece of upland called by the Indians, an island with salt marsh lying between it and the Hill.
Harsimus, from Ahasimus, the meaning is now lost; it was another bit of upland lying south of Hopoghan.
Communipaw, from Gemoenepa, the meaning is not known.
Navesink—a good fishing place.
On July 12th, 1630, Mr. Michael Pauw, Burgomaster of Amsterdam and Lord of Achtienhover, near Utrecht, obtained through the Directors and Councillors of New Netherlands, a deed from the Indians to the land called Hopoghan Hackingh, this being the first deed recorded in New Netherlands. On November 22nd, of the same year, the same parties procured from the Indians a deed to Mr. Pauw of Ahasimus and Aresick (burying-ground), the peninsula later called Paulus Hook. These were the first conveyance by deed of any land in East Jersey. To these tracts Pauw gave the name Pavonia from the Latinized form of his own name, Pauw in the Dutch and Pavo in Latin meaning Peacock. When the first settlement was formed or the first house built is unknown. In May, 1633, Michael Poulaz or Paulusson, an officer in the service of the Company, was living at Pavonia. He probably occupied a hut on the Point which received from him the name of Paulus Hook. In the latter part of 1633, two houses thatched with reeds were built, one at Ahasimus, near what is now the corner of Fourth and Henderson streets, and the other at Communipaw. So far as is known these were the first regular buildings in this county.
Paulusson had charge of the trade with the Indians and was Superintendent of Pavonia. He was succeeded in 1634 by Jan Evertsen Bout, who selected the house at Communipaw for his home, and was the first white resident there; this farm which Bout leased after Pauw[Pg 19] had sold his rights to the Company, was known as Bout's farm, and included all of the upland lying between Communipaw Creek, where the Abattoir stands, on the south, and the meadows where the engine house of the Central railroad stands, or Maple street, on the north. Later the Governor, General Kieft, and the Council gave him a patent for this farm. The house was burned in 1643. It was in commemoration of Jan Evertsen Bout that the circular hill and section of upland at the mouth of Mill Creek was named Jan de Lacher's (or John the Laugher's) Hook. In 1636 Cornelis Van Vorst became Superintendent of Pauw's property and lived in the house built by Pauw at Ahasimus. For several years there was trouble between the Company and Pauw, which was finally settled by the Company paying to Pauw 26,000 florins for his interest in Pavonia.
The Van Vorst Homestead.
Jan de Lacher's Hoeck.
In February, 1643, about a thousand Indians fleeing from the Mohawks came to the Dutch for protection. They were encamped on the upland near the present intersection of Pine street and Johnston avenue. Here, on the night of February 25th, a party of Dutch soldiers, by order of Governor Kieft, murdered and brutally mutilated a large number of men, women and children. The sickening details of this massacre by white Christians cannot be surpassed by the records of savage races. This led to serious troubles; all the Indians united and for a year and a half made war upon the Dutch. They burned the house at Ahasimus in which the widow and family of Van Vorst lived. A portion of the farm-house built on the site of this first house was still in existence in 1895. Between 1649 and[Pg 20] 1655, there were quite a number of patents for lands issued, principally to soldiers, at Communipaw, and as far down as the present town of Greenville, and there were quite a number of flourishing farms at Hoboken, Ahasimus, Paulus Hook and Communipaw. The land upon which they lived was known as Bouweries, and the outlying farms as plantations. At that time the land known as Kavans Point, below Communipaw, extended farther into the bay. Winfield states that "within the present century the waters of the bay have encroached over 200 feet, and that a cherry orchard once stood where fishermen now stake their nets."
In 1655, an Indian girl stole some peaches from a farm near the present site of Trinity Church, New York, and was shot by the farmer. On the night of September 15th, 1655, five hundred Indians made a night attack upon New Amsterdam, being repulsed, they crossed the river and set fire to every house in Pavonia. Twenty-eight farms and outlying plantations with crops and buildings were all destroyed. Of the settlers one hundred were killed, one hundred and fifty were taken prisoners and three hundred were left homeless. For five years the settlements were practically abandoned. According to the Indian laws the title to the lands was again vested in them by right of conquest. In 1658 the Indians made a new deed of the territory to the Dutch. The former settlers who were about to return to their farms asked for exemption from taxes that they might be able to put their farms in order. The petition was granted on condition of their building a fortified village. In February, 1660, a decree was issued ordering all farmers to move their[Pg 21] houses into groups, that might be protected by palisades or stockades, from six to seven feet above the ground. Indian stockades always were of tree trunks, as are those of the Hudson Bay Company to this day. Probably the early Dutch were also, although the later stockades may have been of heavy plank.
On September 8th, 1660, Jaques Cortelyou was ordered to survey Gemoenepa and lay it out into village lots. The village site fronted on the Bay, was two hundred feet deep and extended from what is now Communipaw avenue on the north to the Bay Shore House on the south. The Council ordered that the village should be stockaded, but there seems to have been numerous delays, for in June, 1663, Gerrit Gerritsen, Harman Smeeman and Dirck Claussen were appointed commissioners to fortify Gemoenepa. May 9th, 1661, Egbert Sandersen and Jan Theunissen, inhabitants of Midwout and Amersfoort, L. I., petitioned for leave to erect a saw-mill on a stream at Gemoenepa and move their families there and for a lot of land for each. The request was granted and probably they erected a mill below the Point of Rocks on the stream formerly called the Creek of the Woods and "Creek of the High Woodlands." In papers of 1671, the mill is mentioned as the "Mill of Hossemus;" probably from this mill the creek received its name of Mill Creek. Later Priors Mill was built upon this site and remained until removed and the creek filled in when the cut was made for the Pennsylvania railroad in 1837. In October, 1661, Sandersen asked permission to erect a saw-mill on Showhank Brook; this creek had its rise in an Indian spring in West Hoboken; it ran south until it reached the point where New York avenue crosses Palisade avenue; thence it turned down the hill[Pg 23] through a wild ravine and emptied into Mill Creek. There was a saw-mill on this stream at the foot of the hill, until it was destroyed by fire in 1835.
The first legalized ferry across to Manhattan Island was established at the foot of Communipaw avenue when the village of Bergen was started in the fall of 1660 by William Jansen. The boats were periaugers, the old Spanish pirouge, pointed at both ends, with two masts, but no bowsprit. When horses and carriages were to be transported they were detached and lifted into the boat. The Governor General and Council fixed the rates. Jansen had much trouble, he claimed the exclusive right to transport people and goods to Nieu Amsterdam and objected to people crossing in their own boats. He complained to the authorities at Nieu Amsterdam and the people brought a counter charge against him for refusing to ferry people across; judgment was rendered January, 1663, that "the Sheriff must assist him in getting his pay and that he must do his duty or be discharged." He and his successors ran regular boats three times a week. In 1669 Governor Carteret issued a license to Peter Hetfelsen to run a ferry from Communipaw to New York with a list of the rates to be charged; all of which were payable in wampum. "Any person, letter, packett or message of public business, and the Governor and his family were to be carried free." Hetfelsen was succeeded in 1672 by John Tymensen under the same conditions. From that date there is no mention of the ferry until 1783 when Aaron Longstreet and Company advertised that "constant attendance was given by the boats at the ferry stairs, near the Exchange, at 3 p. m.[Pg 24] to bring passengers to Communipaw where the Newark stage would be ready to convey them to Newark and thence by the Excellent New York and Philadelphia Running Machines in one day to Philadelphia."
The first road built in this county was from Communipaw to Bergen in the fall of 1660. It ran along the present Communipaw avenue to Summit avenue, then northerly along Summit avenue to Academy street; thence westerly to Bergen. It was called the "Off-fall" road, from the stream that ran from Tuers pond and fell over a ledge of rock at the present intersection of Grand street and Communipaw avenue. Until Grand street was extended across the marsh in 1848 the people from Communipaw and along to Bergen Point could only reach Jersey City by way of Bergen, and the Priors Mill road or Newark avenue; where Monticello avenue now is was a marsh until comparatively recent times. On November 24th, 1790, the Legislature appointed five commissioners to locate and build bridges across the Hackensack and Passaic and lay out a road four rods wide from the Newark Court House to Paulus Hook. They were authorized to raise by lottery £27,000, part of which was to aid in completing the road, part to build a bridge over the Raritan, and part in providing suitable buildings for the Legislature.
Communipaw.
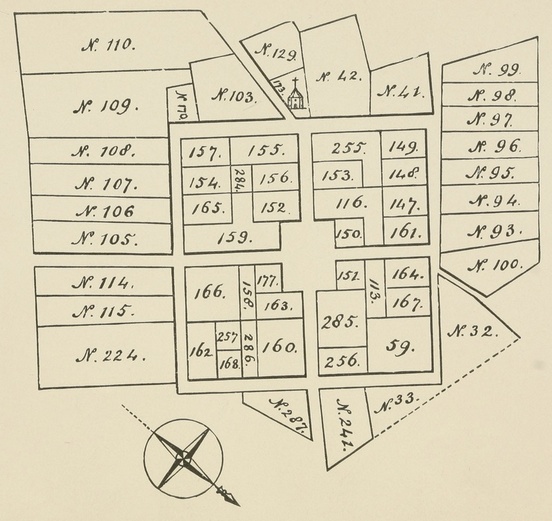
Bergen and Buynten Tuyn.
March 1st, 1660, Tilman Van Vleck petitioned for permission to found a village near the maize land, a clearing and Indian corn field at and around what is now the junction of Montgomery street and Bergen avenue. He was refused and again asked, to be again refused, April 12th. A third application upon August 16th of the same year was successful. It was granted upon the following conditions: "The site should be selected by the Governor and Council; it must be a place easily defended; the land to be distributed by lot, and work on each plot begun within six weeks. Each owner of a lot to send one man able to bear arms. The houses were to be within a fortified village, and the farms were to be outside." It is highly probable that Governor Stuyvesant planned the new village, which was surveyed and laid out by Jaques Cortelyou, Surveyor of Nieu Netherland. This, the first village in New Jersey, was named Bergen, after a small town in Holland, the most important of the provinces constituting the United Netherlands. A square of eight hundred feet on each side was cleared and crossed with two streets that intersected at right angles. A plot in the centre of 160 by 220 feet was reserved for public use. On the exterior of the outer streets now known as Vroom, Idaho, Tuers and Newkirk, surrounding the entire plot, the stockade was erected, with gates at the cross streets, which are now known as Academy street and Bergen avenue. This was completed in 1661.[Pg 26] Tradition states that on the corner of Vroom and Tuers streets was built a block house as a protection against the Indians. It was near the first church. Winfield thinks that the houses were of logs and probably thatched with cattails. It is an interesting fact that the first lot taken in the new village, now known as 201 Academy street, was bought by Cornelis Van Reypen, 1st. The house now occupied by Mr. Cornelius Van Reypen, 3d, is the second upon the lot, which has always been in the possession of and the home of the lineal descendants of the founder of the family in Bergen. It is also true of the Van Wagenens, Romeyns, and Van Winkels on Academy street, that they are living on the lands allotted to their ancestors at the founding of Bergen, which have never passed from the family possession. Representatives of the Sip and Newkirk families also still hold ancestral lands. In this respect Bergen has quite an exceptional record for an American town.
Here in Bergen the first local Court in New Jersey was organized in September, 1661, with Tielman Van Vleck as schout or sheriff, and Michael Jansen, Herman Smeeman and Casper Stynmets, as schepens or magistrates, something like justices or aldermen. The schout was afterwards authorized "to fill and execute the office of auctioneer." All criminal cases were referred to the Director General and Council of Nieu Netherland. Only minor offenses, such as brawls, slanders, scolding, threats, etc., could come before this Court. On July 19th, 1673, Mr. John Berry's house in Bergen was made "ye prison for the Province," until a house could be built for that purpose, and Adrian Post, the constable, was appointed keeper. Later a "lock up" was built on the easterly side of the square near the school-house. On the westerly side were the stocks and the whipping post. The stocks were still standing in 1824, and even later, and the whipping post was a terror to evil doers as late. In 1662, a well was dug in the center of the square. Troughs were placed around it for the use of the cattle, and a long sweep used to raise the water. This well was used into the present century, when it was covered and during the war of 1812-14 a liberty pole was erected in it. In 1870, when the square was paved the pole was taken down and no trace of the well is left.
Engelbert Steenhuysen was the first schoolmaster in Bergen, having been licensed October 6th, 1662. He[Pg 28] was allowed two hundred and fifty guilders in wampum annually and "some other stipulations beside the school money, as reason and equity shall demand." It seems that he was required "to look out and procure a suitable place in which to keep the school." According to the Albany records (vide Winfield) the people of Bergen addressed a memorial to the Council that he might be obliged to fulfill his contract to act as Voorleezer and Schoolmaster for two years. The church records do not mention him as Voorleezer. In 1664 the first school-house was built on the lot set apart for school purposes on the northeast corner of the square. Mr. Winfield states that this school-house was of logs, but from the records in the Deacons Account books it evidently was not. It is not known positively whether it was of stone, brick, or frame, but several entries of "lbs. of nails," "whitewashing" and "nailing boards in the gable," are included in the account of work and repairs upon the building. Whatever it was, for about fifty years it was used, and then a new school building was erected on the site of the first. The records state that, "On Tuesday, May 11, 1708, Mathews Bensum had made a foundation, and Mr. Adrian Vermuelen, Voorleezer at Bergen, laid the corner stone."
The following is the itemized account of the expenses incurred:
| st. | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1708 | To Adrian Quackinbush for 100 boards at 28 st. apiece | ƒ140 |
| " | To Mathew Bensum, 10 days at 10ƒ per day; mason | 100 |
| " | To Martin Winne, 21 days at 10ƒ; mason | 210 |
| " | [Pg 29]To Risso, the hod-carrier, 21 days at 3 realtje per day | 95.10 |
| " | To 6 lbs. nails at 3ƒ per lb. | 18 |
| " | To the glazier, 23 feet of glass | 69 |
| " | To Samuel Bayard, for 84 lbs. nails at 3ƒ per lb. | 252 |
| " | To 5 lbs. nails at 3ƒ per lb. | 15 |
| " | To lock for the door | 7.10 |
| —— | ||
| Total for 1708 | 907 | |
| 1710 | Expended over 1708 | ƒ907 |
| May 3 | To Mathew Mott for iron work | 84 |
| " | To Helmigh Roelofse for paving stone (steen blinkers) | 86 |
| " | To Cornelis Van Vorst, 2 lb. nails at 3ƒ per lb. | 6 |
| " | To Hendrik Clausse Kuyper for 4 lb. nails | 12 |
| " | To Gerrit Stynmets for 4 lb. nails | 12 |
| Oct. 3 | To Gerrit Roose for laying the ceiling | 40 |
| " | To his board | 6 |
| " | 10 lbs. nails | 15 |
| " | To 10 boards at 36 stivers apiece | 18 |
| " | For carting the boards | 7.10 |
| —— | ||
| Total cost | ƒ1,193.10 |
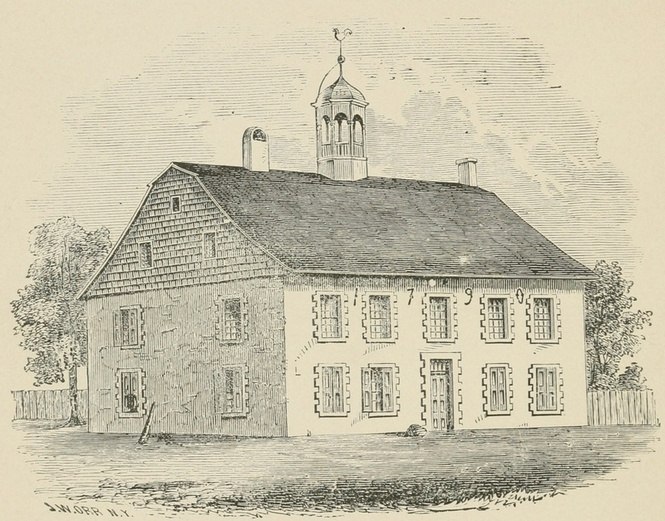
Columbia Academy.
Several citizens, evidently gratuitously, carted materials to the site, in all sixty-three loads of stone, twenty-one loads of clay, five loads of sand, one load of lime. Repairs were made in 1782. In 1790 the Columbia Academy was erected on the same site and stood until 1857, when the present school-house, No. 11, was built. In the rear wall of this building are many of the stones used in the old Academy and it is ornamented with the same weather vane that adorned the former building. Tradition states that this is the veritable weather vane that first surmounted the steep roof of the Octagonal Church, then was removed to the[Pg 30] second church, from which it was placed on Columbia Academy when the present church was erected in 1841.
In the early days of the little settlement, religious services were undoubtedly held in the school-house, and in the absence of a minister were conducted by the Voorleezer or clerk. In 1662 the schout and schepens of the village petitioned the Council for a minister, stating that certain persons had pledged themselves to subscribe four hundred and seventeen guilders in wampum annually for the support of a minister. But there was no local pastor of this first church in New Jersey until 1750. Until then the pastors from New York came over at stated times of the year, very often during week days, to administer the sacraments of Baptism and the Lord's Supper, admit new members, install the elected elders and deacons and to conduct special services. Also pastors from Long Island, Esopus, Fishkill, Tapan, Raritan and other places preached occasionally at Bergen. These visiting pastors received from the Bergen congregation from twenty-five to seventy-two guilders per service besides expenses and board. The accounts show that the New York ministers paid six guilders for ferriage and six guilders for a carriage from the ferry to Bergen. Twelve guilders for board was charged after every visit of a minister. From 1672 to 1680 Domine Van Nieuwenhuysen preached and administered the sacraments at Bergen three times a year on week days, for which he received "thirty bushels or fifteen bags of wheat."

The "Little Church."
In 1680 the first church building was begun in Bergen, the total cost so far as it is possible to get at the figures, was two thousand six hundred and twelve guilders. It was an octagonal stone building with the roof sloping to a point and surmounted with a vane bearing a rooster. The windows were placed very high. In the summer of 1683 the first bell was placed in the high pointed roof, probably a gift from some of the members. The bricks in the windows and arch over the door were brought from Holland. Over the door was a stone with this inscription: "Kirk Gebouwt in Het yaer 1680." Domine Taylor gives an interesting description of the interior of the "little church" as it is often called in the account books. "The bell-ringer stood in the center of the church. Pews were placed around the walls and occupied only by the men; the women sat in chairs. The pulpit was high and reached by stairs; below and in front of the pulpit was a little pew with a book-board in front of it for the use of the Voorleezer, who had a long rod with a slit in the end which he reached up to the minister, who inserted in the slit notices to be read." The collections were in wampum for many years, and it was one of the duties of the deacons to sell the wampum to the heads of families, who each distributed it among the members of his family and they deposited it in the collection bags. These bags were of black velvet attached to a long pole. At the bottom of each bag was a small bell to arouse[Pg 32] the people at collection time. The bags were hung on hooks in a suitable box beside the pulpit near the deacons' seat; at the proper time the deacons each with bag in hand presented themselves before the pulpit, received their charge from the minister and then went among the congregation and made the collections. The bags were spoken of as "the bell." This custom continued until 1800.
The first pall the church was able to buy, cost, according to the Deacons account:
| 10 el of black cloth at 24ƒ per el | ƒ240 |
| A linen cover to protect the pall | 14 |
| —— | |
| Total | ƒ254 |
It was first used at the funeral of Engelbert Steenhuysen, January 16th, 1678. The rent of the pall was quite a source of income to the church. The price to an adult was fourteen guilders and to a child seven guilders, until June 14th, 1715, when it was reduced to six guilders for an adult and three guilders for a child. On January 17th, 1715, the second pall was bought for one hundred and ninety-five guilders, and the old one probably refitted to use at the burial of children. On January 1st, 1798, a fine large pall was bought for £5 11 s., 3 d. and a small one £2, 13 s., 10 d. The cost of the bier used at funerals was usually seventeen or eighteen guilders, and one lasted five or six years. On May 26th, 1678, Bergen's first communion set was bought at an expense of seventy-four guilders and ten stivers, and consisted of the following articles: "Eight pounds of pewter, being three plates and a pitcher of 6 guilders the lb., and two pewter beakers at 12 guilders apiece, and one el of Osnaburger linen." At the same time 11 el linen was bought for a table cloth, costing 5 guilders 10 stivers per el, or 60 guilders 10 stivers for the whole. On January 26th, 1731, the[Pg 34] pewter cups were changed for two silver ones, bought of Hendrikus Boele and costing five hundred and nineteen guilders and ten stivers in wampum. The latter cups are still used at every communion service of the Bergen Reformed Church. A large Staten Bible was bought in 1620, costing sixty guilders and was probably used until the services were conducted in English.
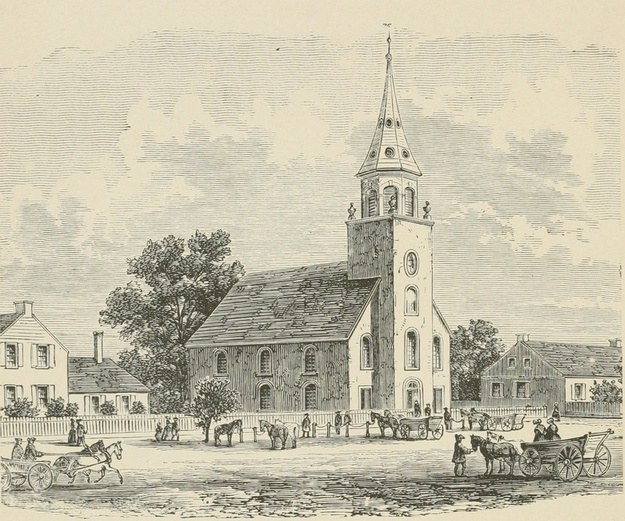
The Second Church.
In 1773 a new church building was erected in the second cemetery, which had been opened in 1738, on the southwest corner of Vroom street and Bergen avenue. It fronted Bergen avenue, about the center of the east side of the lot. The stone above the door of the first church was placed above the door of the second building with a stone beneath with the inscription: "Her bowt in Het yaer 1773." Both are now over the door on the south side of the present church building on Bergen and Highland avenues of which the corner stone was laid August 26th, 1841. This site is part of the land originally reserved for the pastor's use. In the walls of the present church are many of the sand stone blocks from glacial bowlders that were formerly built into the walls of the earlier church buildings. The third church was dedicated July 14th, 1842. The dedication sermon was preached in Dutch and understood by many of the congregation. Mr. Versteeg, in his translation of the Church Records states that Dutch ceased to be the language of the pulpit and of the church records May 26th, 1793, when Mr. John Cornelison was ordained and installed as pastor, although in some instances English and Dutch were used alternately in the records as late as 1805. Old residents tell me that they have heard occasional sermons in Dutch at a very much later date. In "The Annals of the Classis and Township of Bergen," Domine Taylor states that "singing in Dutch was discontinued about 1809, but[Pg 36] preaching in Dutch continued for some time later." Two of the hymns sung at the dedication of the new church were composed by Mrs. Anna R. Taylor, wife of the pastor, the Rev. Benjamin C. Taylor. In the early days the Bergen Reformed Church required of the applicants for membership a very rigid examination before the minister and consistory in Bible history, evidences of the truths of Christianity, and the Doctrines of the Church as set forth in the Heidelburgh Catechism. The young people went at least once a week to "Catechism" to the pastor, the Voorleezer or an elder, until perfectly familiar with the Catechism.
In the early Dutch Churches on Long Island there was an officer called Krank besoecker—Sick Visitor, also sometimes called Zieck-trooster—the Sick Consoler, or Comforter; undoubtedly the same office existed in the early Bergen Church, but if so whether it was filled by the Voorleezer or some other member of the congregation I cannot say. The name of "Sick Consoler" is very suggestive of kindly brotherhood, expressing much more than the modern name of the same office.
The Voorleezer was a very important official in the Reformed Church and combined the duties of several offices. 1st, as Voorleezer or clerk, upon Sundays, before the minister entered the pulpit, the Voorleezer took his place at the desk in front of the high pulpit or "preaching chair," as it was called, and opened the services by announcing and reading a verse from the Psalms. He then led the congregation in the singing of it, which gave him the title of foresinger. After the verse had been sung he first read the ten commandments or the creed, and then a portion of the Scriptures. In the meantime the preacher had ascended the pulpit, a verse was again sung and the Voorleezer went to his seat in the pew set apart for the consistory. When the sermon, which usually lasted an hour and a half, was half finished the minister announced a Psalm verse, the foresinger returned to his desk and led the singing, while the deacons went around with the "bell" to gather in the collections. At the close of the services the Voorleezer again led in singing and the minister dismissed the congregation with the benediction. 2d, during the week days, the Voorleezer taught the village school, and was at the same time catechiser, using in early days of Bergen a question book written by Domine Johannis Megapolensis of Nieu Amsterdam. If there was no minister the Voorleezer took the place of a local pastor in all respects except baptizing children and administering the Lord's Supper. Not being[Pg 38] allowed to ascend the pulpit he read sermons from his desk. (Among items charged in the Deacons Accounts were several books of sermons.) On Sunday mornings he held a service at Bergen and on alternate Sunday afternoons at some farm-house in Ahasimus and Communipaw. An hour-glass stood on the reader's desk and when the sand had run from the upper into the lower hollow he was to suspend services and dismiss the congregation.
He officiated as bell-ringer, kept the church records, took care of the Communion set, which his wife kept clean, the bier, and the pall, acted as bookkeeper for the Deacons and also served as Aanspreker or funeral director, in which capacity he kept the records of the dead. For services as Voorleezer and schoolmaster the salary exceeded ƒ600., and as bookkeeper and Aanspreker he charged for his services, and probably received extra fees for baptismal and marriage records. The first Voorleezer mentioned in the church records was Regnier Bastianse Van Giesen who served in that capacity from 1665 to May 12, 1707, when he died. He probably came from Utrecht in the Netherlands, lived awhile at Midwout, L. I., then came to Bergen. He was an educated man who wrote the language correctly and was evidently versed in the history of his country. These Voorleezers were men of great influence in the early days of Bergen, especially before there was a settled pastor. The office continued until 1789 when Mr. John Collard received the title of Clerk with the salary of £2, 15s. per annum.
After the receipts of the church began to exceed the expenditures the Deacons invested the surplus funds[Pg 39] in cows which were rented out to responsible members of the congregation for 12 lbs. of butter per annum or its value in money. In 1679 butter sold at 22 stivers per lb. and the rent for one cow was 13 guilders, 4 stivers. After 1715 the Deacons gave up the "butter rent" business and loaned the church funds at 6% on the bond of the borrower and his securities, or upon personal property to the value of the sum loaned given as collateral security. In the early days for more than a century, accounts were reckoned in "guilders seewan" and wampum often accumulated in quite large amounts in both loose and braided. In 1691 ƒ4,000 in wampum was taken to Stephen Van Courtlandt to be exchanged for silver money. The Church Treasury has a package of $1,214 in Continental bills and $700 in worthless State and communal paper of still earlier date.
Until October 3, 1681, all marriages in Bergen were performed in the school-house, thenceforth in the church, it was the custom to be married in the presence of the congregation either by the minister or the Voorleezer, if by the latter, the record bore the clause "in the presence of the Court of Bergen." In the early days the usual fee was ƒ6 in wampum, paid over to the church funds. Often a collection was taken up among the wedding guests for the poor. There are several instances of the kind on record. There was no almshouse until recent years, and in the early days the town paid for the board of the poor, but the method of arranging the matter sounds very strange nowadays. It seems from the records that the poor dependent upon the town were sold to the lowest bidder. Winfield quotes the following: "At Bergen Town meeting Dec. 15th, 1784, at a public Outcry is sold Enoch Earle to the lowest bidder for the sum of seven pounds, ten shillings, the conditions are as follows, the byer is to find the said Enoch Earle a Good Bed, Washing, Lodging and Victuals, and mending his close; the Overseers of the Poor are to find all the New Close and then the said Enoch Earle is to work for the Byer as much as he is able to do until the year's End."
The burial customs were probably the same as those of their fatherland and very peculiar in some respects. The most important character was the Aanspreker, upon whom rested the whole responsibility of the affair. Immediately upon a death he was notified, and at once repaired to the sterfhuis (house of the deceased) with a few sheets of mourning paper, upon which he took down the names of friends to be notified of the death, and marked those who were to be invited as bearers or as mourners. Until after the funeral he had full charge of all details. If necessary he appointed assistants, in case the deceased was very rich or very prominent there were often ten or even twenty Aansprekers employed to announce the death, and one, usually an old servant of the family, went in the middle of the street, walking slowly with bowed head and face buried in a large mourning handkerchief and led by two Aansprekers, one on each side, while the others were doing the "wete" or announcement at the houses. On these occasions all were dressed in low shoes, black stockings, black knickerbockers, a black cutaway coat covered by a long, flowing black mantle, with a white cravat or bands and a queer looking three-cornered hat or "steek," from one corner of which to the right floated a long black crape streamer, whilst upon the left corner was pinned a rosette showing the sex of the deceased and if married or single.
At the funeral all gathered at the sterfhuis, the[Pg 42] closest friends a little earlier, who were served with beer or spirits and long clay pipes or segars; when all were gathered the chief Aanspreker made a few consolatory remarks or offered a prayer, then signalled the bearers to carry out the bier and martialed the relatives and guests in order, the youngest members of the family coming first. All the mourners and bearers, and sometimes the driver of the hearse, were either dressed as the Aansprekers or else wore rosettes pinned upon the sleeve or lapel of their coat. The Aanspreker wore white or black gloves according to the sex of the deceased. One or two Aansprekers led the procession, the bearers walked beside the hearse; if there were other Aansprekers, they went between the hearse and first carriage and the procession slowly wended its way to the cemetery. All people meeting a funeral stood still with bowed head and doffed hat until at least the hearse had passed; at the cemetery gate the bearers bore the coffin to the grave, and the Aanspreker made a prayer. After the coffin was lowered and covered with earth, all filed out in the same manner as they had come and returned to the sterfhuis. Here refreshments were served by the women, who as a rule did not go to the cemetery.
To be buried within the church, in or before the baptistery, was a great honor and showed deep veneration by the congregation and was usually accorded only to ministers or men prominent in the church, an extra price being paid for the privilege. The record is effaced of the first burial within the Bergen Church; but the second was a little daughter of Enoch Michielse Vreeland on August 1st, 1682; the third, on September 4th[Pg 43] of the same year, was Peter Mercelis. On June 21st, 1683, was "buried the corpse of Maekje Baltusen, daughter of Baltus Bartensee, the sixth in church, and the first with knell." The last burial in church mentioned in the records, was that of "Anntje Jackson, aged forty-nine years, who died on Friday, January 13th, 1738, at about 8 A. M., and was buried on Sunday, January 15th, in the church in the baptistery." It was not compulsory that interments should be made in the cemetery or church and many burials were made upon bouwerijen or farms. It was an old Dutch custom lasting until quite recent times, to have burial clothes prepared and kept in store for each member of the family.
The following account of the burial of a pensioner of Bergen Church is dated 1690:
| Coffin and spirits | ƒ25.10 | seewan |
| 1/2 keg of beer | 15.16 | " |
| Flour and milk | 6.05 | " |
| Sundries | 15.05 | " |
| Aanspreker | 19.10 | " |
| Mathew Cornelinsen for carting the goods | 3.00 | " |
| —— | ||
| Total | ƒ85.06 | " |
The first cemetery of Bergen was on the south side of Vroom street, just outside of the southeast corner of the palisade of the new town, where it is said there was a little fort for protection against the Indians. In this burial ground the first church was built, on the site now occupied by Dominie Cornelison's family vault, and fronting on Vroom street, facing Tuers avenue. After the cemetery had been used over seventy years, in 1738 the second burying ground was opened on the southwest corner of Vroom street and Bergen avenue. These older cemeteries were not laid out in family lots, but the graves were made in any place convenient, and thus the last resting places of the different members of a family were seldom near together.
For nearly two centuries these two burial grounds were the only ones in this vicinity. In the fall of 1829 an episode occurred which led to the opening of the Jersey City Cemetery. One morning a passer-by saw the body of a drowned man washed ashore at Harsimus; he drew it up on the grass, and after a little several others gathered there and in the discussion that followed it was decided to give the body suitable burial and mark the grave with a stone that it might be identified in case any friends of the dead man might eventually be found. The little group contributed a sum sufficient, as they supposed, to make the desired provision, and a committee was appointed to attend to the matter, and see that the body was properly buried [Pg 45] in the cemetery of the Bergen Church. The sexton charged $12 to open a grave, which seemed to the people of Jersey City such an enormous price that it aroused universal indignation, which resulted in a public meeting at Hugh McCutcheon's Farmer's Hotel at 42 York street (quite a celebrated tavern of the day), at which it was decided to open a new cemetery and no longer be dependent upon that of the Bergen Church. Subscriptions were taken and a cemetery company was formed of which David C. Colden, one of the associates, and at that time Mayor of New York, was President, Robert Gilchrist was Treasurer, and J. D. Miller was Secretary. The result was the purchase of five and a half acres on the hill-side south of the Newark Turnpike, and the Jersey City Cemetery was opened, at that time a quiet, country place, where under the drooping willows, many families, prominent in the early life of Jersey City were laid to rest far from the noise of the young city; but with the passing years, the city has extended out to and far beyond their resting place, all about them are city streets and a railroad now runs along at the foot of the hill.
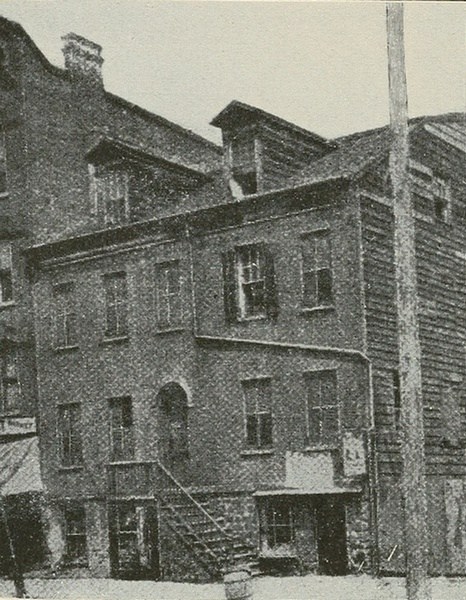

The Old M'Cutcheon Hotel.
In 1831 or thereabouts, the third burial ground of the Bergen Church, east of Bergen avenue and south of Vroom street, was bought of Aaron Tuers for $500, and surveyed and laid out in fourteen foot lots by Colonel Sip. These lots were sold at $5 each, the gore lots being reserved for the poor. In 1849 the New York Bay Cemetery was opened; it is one of the largest Protestant cemeteries in the county, embracing about one hundred acres, sloping to the waters of the bay, a very beautiful location on Ocean and Garfield avenues.[Pg 46] About 1857 Abraham Spier, while acting as sexton for the Bergen Church, laid out a burying ground south of and adjoining the west end of the second church cemetery, which is still known as Spier's Cemetery. Since then the Catholics have opened a cemetery south of Communipaw avenue, and west of West Side avenue. Jersey City has other cemeteries outside of the city limits, of more recent organization.

Paulus Hook from Harsimus in 1823
Paulus Hook was a circular piece of upland lying east of what is now Warren street, and consisted of sand hills, some of considerable height. On the north was Harsimus Cove, First street; on the east the river, on the south Communipaw Cove, South street; and to the west, salt marsh, which was covered with water at high tide. It was sold by the West Indian Company to Abraham Isaacsen Planck, May 1st, 1638, for the sum of four hundred and fifty guilders, calculated at twenty stivers to the guilder. It remained in the Planck family until August 2d, 1699, when it was sold to Cornelius Van Vorst for £300 "current money of New York." During this time it was used as farm land until 1794, as most of it continued to be until 1804.
Early in 1764 a new Post route was established between New York and Philadelphia, and Abraham Messier, who owned a wharf at the foot of Cortlandt street, New York, and Michael Cornelissen made arrangements with Cornelius Van Vorst for a landing at Paulus Hook (foot of Grand street.) The boats were two periaugers, which made the trips across the river "as the wind served." The Ferry Company was to keep in repair the causeway leading out to the road to Bergen. The new Post route to Philadelphia was by way of Bergen Point and Staten Island. Formerly travellers from New York to the south had gone by boat to Amboy, thence by stages to Philadelphia and other[Pg 48] points. Just when the Post route was changed I have been unable to ascertain, but in 1715 commissioners were appointed to lay out a road across the meadows, intersecting the Bergen Point road, with ferries across the Hackensack and Passaic. The road was nearly the same as the one since known as the Newark plank road. Mr. Thomas Brown, one of the commissioners, owned the land from New York Bay to Newark Bay. He owned what is known as the Gautier house, and on his land on Newark Bay side built the ferry known as Brown's ferry. After the completion of this road and ferries the Post route came by the mill and church road to Bergen, thence by the road across the meadows. The stages stopped over night at Princeton.
Van Vorst laid out a small park, semi-circular in shape, at what is now the foot of Grand street. Michael Cornelisen built a tavern just north of Grand street, near the water, a low frame house about forty feet in length, with a porch in front over which projected the extended Dutch roof. In 1800 this house, used as a tavern and ferry-house, with several spacious barns, stables and a store-house, were the only buildings on the Hoeck. In 1769 Van Vorst laid out a race course one mile long around the sand hills and along the edge of the upland; this was in use, except during the war, until the founding of Jersey City in 1804. This was the only race course in Jersey City until the Beacon Race Course was established on the Hill in what was later Hudson City, about 1837-38, and discontinued about 1845. It was located southeast of where the reservoir now stands and was the scene of some very celebrated races. It was here on August 1, 1839, that[Pg 49] Dutchman, trotting against time, made three miles in seven minutes, thirty-two and a half seconds. Hiram Woodruff claimed that he could have done it in seven minutes, twenty-seven seconds, or better; this record was not beaten until by Huntress at Prospect Park, September 21, 1872.
The ferry was leased to several different parties. In 1771 Abraham Messier obtained a lease for three years; this was renewed in 1774 and as he died soon after his widow remained in charge, probably during the war subject to military control. Soon after the war her name is connected with the ferry, and in 1786 she petitioned for repairs to the ferry stairs on the New York side.
In the early spring of 1776, Lord Stirling, then in command of the American forces in this locality, took measures to put Bergen and Paulus Hoeck in condition of defense, and to open means of communication with the interior of the State. A fort was built at Bergen Neck, later called Fort Delancy, to prevent the English from coming over from Staten Island. It was located on the rising ground now bounded by 44th and 45th streets and Avenues B and C in Bayonne, one quarter of a mile below the canal. After it was given up by the Americans it was held by the Tories until September, 1782. Lord Stirling personally examined the grounds and proposed to have the militia of Bergen, Essex, and Middlesex counties build broad, good roads from Paulus Hoeck to Brown's Ferry on the Hackensack, and from Wiehawken Ferry to Hackensack Ferry. Upon the arrival of Washington, the immediate construction of works at Paulus Hoeck was ordered as "of great importance." These were soon completed and troops from New York and Pennsylvania stationed there, under command of General Mercer, the veteran of Culloden and De Quesne.
On July 12th, 1776, the batteries of the new fort opened fire on the British men of war, the Phoenix of forty guns and the Rose of twenty guns, as they came up the Bay to New York. The fire was returned with broadsides as they passed. That same evening Lord Howe sailed up the harbor to New York. Troops were[Pg 51] stationed at Paulus Hoeck and Bergen ready to reinforce Washington. After the battle of Long Island these orders were countermanded and the troops were stationed at Paulus Hoeck and Bergen Neck. On the 15th of September, the British captured New York City and again the Paulus Hoeck troops had a little skirmish with the enemy. Occasionally Washington came over from his camp at Harlem to reconnoiter along the Jersey shore as far as Paulus Hoeck. Recognizing that the fort could not be held, preparations were made for its evacuation. General Mercer removed all guns, stores and troops with the exception of a small guard under orders to leave upon the first appearance of the enemy. On the afternoon of September 23d, 1776, the English ships cannonaded the fort for half an hour or more, then landed a force. About twenty boats also came over from New York. They found nothing but a few guns unfit for use. General Mercer and his troops retired to Bergen with an outpost at Prior's Mill. October 5th, the American troops left Bergen to join Washington in his retreat to the Delaware.
For a long time Paulus Hoeck was the only British stronghold in New Jersey. They greatly strengthened the defences built by the Americans and made their landings at this point. At high tide boats could pass over the marsh and even over the causeway that connected Paulus Hoeck with the main land. An elevated foot path or board walk had been made parallel to the road to enable people to pass at all stages of the tide. This was still in use well into this century.
I quote Mr. Winfield's description of the fort: "It[Pg 52] was a very strong position with the waters of the river and coves on the north, east and south, and on the west a marsh, with a creek running near the westerly edge of the upland from near Montgomery street southwesterly into the southerly cove near the foot of Van Vorst street. This creek had been connected with the Harsimus cove by a ditch about on the line of Warren street. Over this ditch on the line of Newark avenue was a drawbridge with a barred gate. Thirty paces inside of the ditch and the creek was a row of abattis extending into the river. The main works were in the line of Sussex street extending from about St. Mathews Church easterly to Greene street. The barracks were at the intersection of Essex and Warren streets. From the main fort a redoubt extended southerly along Washington street to a half moon fort on the southerly side of Essex street. There was one fort on the north west corner of Grand and Washington streets. Some block-houses had been constructed north of the main works, and one of them north of the road leading to the ferry. The burying ground was on the west of Washington street, extending from Sussex to a short distance south of Morris street."
At four o'clock on the afternoon of August 18th, 1779, Major Henry Lee, with four hundred infantry and a troop of dismounted dragoons started from New Bridge (Hackensack), on a march of fourteen miles through the woods to make an attack upon the fort at Paulus Hoeck. He detached patrols of horse to watch the communication with the North River and stationed parties of infantry at different roads leading to Paulus Hoeck. At Union Hill he filed into the woods where by the guide's timidity, or treachery, the march was prolonged to three hours before gaining the right road. The same night Colonel Van Boskirk left Paulus Hoeck with a force of one hundred and thirty men to make a raid upon the English neighborhood. Fortunately the two parties did not meet. Major Lee and his men reached Prior's Mill at 3 A. M., August 19th; at 3:30 they reached the ditch at the intersection of Newark avenue and Warren street. The tide was rising but Lieut. Rudolph found the canal fordable, and led by Lieuts. McCallister and Rudolph the troops pushed through and soon gained possession of the outer fort. Major Sutherland, who was in command of the fort, retired into a small redoubt with a few officers and forty Hessians. It was nearly daylight and Major Lee had no time to dislodge them. He had intended to burn the barracks, but on finding sick soldiers, women and children in them he refrained. He retreated, carrying with him one hundred and fifty-nine prisoners, officers[Pg 54] and men; he lost two men killed, and had three men wounded.
Captain Forsyth was ordered to Prior's Mill to collect such men as were most fit for action and take a position on Bergen Heights to cover the retreat. This position was in the woods near Bergen and Sip avenues, said to be about the site now occupied by Dr. Hornblower's house, 631 Bergen avenue. Dr. Hornblower's grandmother was then a little girl, Anna Merselis, and that morning in looking for a cow, she came upon Lee's soldiers, who detained her while they waited, to prevent her carrying any report of their presence to possible enemies. The troops remained there until messengers had been sent to ascertain if the boats that Major Lee had arranged to have in waiting for him at Dow's Ferry were there. He had intended to cross the Hackensack and by the Belleville Turnpike reach the high ground east of the Passaic, and thus return to New Bridge; but the boats had been removed to Newark, and Major Lee with ruined ammunition and tired men, encumbered with prisoners, was obliged to return by a route liable to be interrupted by troops from New York. With undaunted courage and wise precautions the brave troops started on the return march of fourteen miles to New Bridge; at "Weehock" Captain Catlett came up with fifty men and good ammunition. At the Fort Lee road Col. Ball met him with two hundred fresh men, and Major Lee and his men safely reached New Bridge about one o'clock in the afternoon. The English were greatly annoyed and the Americans exceedingly jubilant over the affair.
In a letter to Congress General Washington said:[Pg 55] "The Major displayed a remarkable degree of prudence, address and bravery upon this occasion, which does the highest honor to himself and to all the officers and men under his command. The situation of the fort rendered the attempt critical and the success brilliant." On the 24th of September, Congress passed the following resolutions respecting the affair:
"Resolved, That the thanks of Congress be given to His Excellency General Washington for ordering with so much wisdom, the late attack on the enemy's fort and work at Powles Hook.
"Resolved, That the thanks of Congress be given to Major General Lord Stirling for the judicious measures taken by him to forward the enterprise and to secure the retreat of the party.
"Resolved, That the thanks of Congress be given to Major Lee for the remarkable prudence, address and bravery displayed by him on the occasion; and that they approve the humanity shown in circumstances prompting to severity as honorable to the arms of the United States, and correspondent to the noble principles on which they were assumed.
"Resolved, That Congress entertain a high sense of the discipline, fortitude, and spirit manifested by the officers and soldiers under the command of Major Lee in the march, action and retreat, and while with singular satisfaction they acknowledge the merit of these gallant men, they feel an additional pleasure of considering them a part of an army in which very many brave officers and soldiers have proved, by their cheerful performance of every duty under every difficulty, that they ardently wish to give the truly glorious examples they now receive.
"Resolved, That Congress justly appreciates the military caution so happily combined with daring ac[Pg 56]tivity by Lieuts. McCallister and Rudolph in leading on the forlorn hope.
"Resolved, That a medal of gold emblematical of this affair be struck, under the direction of the Board of Treasury, and presented to Major Lee.
"Resolved, That the brevet and the pay and subsistence of Captain be given to Lieuts. McCallister and Rudolph respectively."
Congress also placed in the hands of Major Lee $15,000 to be distributed among the soldiers engaged in the attack. On one side of the medal awarded to Major Lee is a bust of the hero, with the words "Henrico Lee, Legionis Equit Praefecto, Comitia Americana. The American Congress to Henry Lee, Colonel of Cavalry." On the reverse, "Non Obstantib fluminibus vallis astutia et virtute bellica parva manu hostes vicit victosq armis humanitate devinxit. In mem. pugn. ad Paulus Hook, die XIX August, 1779." "Notwithstanding rivers and entrenchments, he with a small band conquered the foe by warlike skill and prowess and firmly bound by his humanity those who had been conquered by his arms. In memory of the conflict at Paulus Hook, nineteenth of August, 1779."
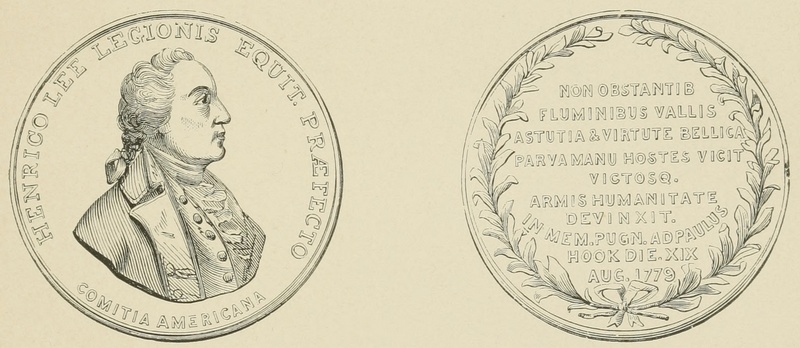
The Lee Medal
The King of the Woods.
On August 24th, 1779, General Lafayette and his troops marched on a foraging expedition from near Fort Lee to Bergen. On the morning of the 25th they arrived at the brow of the Hill and encamped about the large, old tulip tree, known as "oude Boom" to the early settlers and as the "King of the Woods" to those of later date. The locality is now known as Waldo avenue, between Henry street and Magnolia avenue. The tree was cut down December 20th, 1871. Lafayette's headquarters were at the Van Wagenen place on the northwest corner of Academy street and Bergen square. Mr. Taylor states, "in the orchard on the old parsonage site on northwest side of Square," where he entertained at dinner General Washington who came over from Hackensack. The dinner was cooked in the Van Wagenen weave-house and eaten under an apple tree. This tree was blown down in a gale on September 3d, 1821, and from a portion of it was made a very handsome cane, gold mounted and with this inscription, "Shaded the hero and his friend Washington in 1779; presented by the Corporation of Bergen in 1824." When Lafayette visited America in 1824, when he was on his way from Jersey City to Newark, there was a gathering of all the people of this vicinity to meet him at Riker's Tavern, Five Corners, which is still standing on the southwest corner of Newark and Summit avenues. Upon this occasion[Pg 58] Domine Cornelison presented him with the cane, making a very appropriate address.
The farmers living near Guttenburgh during the Revolutionary War were ostensibly neutral, as the roads were often traversed by the soldiers of both parties. Stories are told of the bare and bleeding feet of the Americans cut by the sharp rocks, and many traditions of interest are connected with different places in that locality; notably with the old homestead known as the "Lake property." The story of one tragedy with a touch of the absurd, should be preserved. One bitter cold night in the winter of 1777-78, after all of the family in the old stone farm-house on the Lake property, except the good haus-frau, had retired to their beds, while she was still busy in the kitchen arranging her earthenware jars of milk before the wide fire-place preparatory to the morrow's churning, she was startled by the entrance of a party of English scouts who had come over from New York and attracted by the firelight shining through the wide kitchen window, had stopped to warm and rest awhile, leaving their horses tied to the trees. While they were enjoying the spirits in their flasks and the comfort of the fire, a party of American scouts that had come down the Hudson to reconnoiter, came along and seeing the tethered horses outside and the group of redcoats within, opened fire upon them through the window, killing them all. In the melee the milk jars were broken and the milk mingled with the blood of the dead scouts covering the floor. The old lady was terribly frightened, but her new guests came in and carried out the dead, and as the ground was frozen hard, buried them[Pg 59] under the deep snow at some distance from the house; then they brought water from the well and asking for brooms scrubbed up the floor, and brought in fresh piles of wood and building up a great fire made themselves comfortable until daylight. Before leaving they made up a little fund to compensate their hostess for her broken jars and wasted milk.
After Andre's execution General Washington formed a plan to seize Arnold and bring him to the Jersey shore, first to punish him, second to exonerate from suspicions of treachery another of his Generals, St. Clair. Major Lee persuaded Sergeant Major John Champe of Loudon, Virginia, to attempt to carry out the plan. He was to desert to the British, join Arnold's American Legion and if possible bring Arnold within reach of American troops. About 11 o'clock on the night of October 20th, 1780, he started upon his perilous adventure; within half an hour his absence was discovered and reported to Major Lee who delayed the pursuit as long as he possibly could, but a little after twelve, troops started after the supposed deserter. At Union Hill Champe was only a short half mile ahead. Knowing that his flight to Paulus Hook would be intercepted, he started for the British patrol boats lying in Newark Bay near Brown's Ferry (near the Newark plank road). His pursuers were within two or three hundred yards of him, when he dismounted and running across the meadows plunged into the Bay and swam for the boats, calling for help. The British sent a boat for him and fired upon his pursuers. He soon established the innocence of the other Generals and sent word to Lee to meet him at Hoboken upon a certain night when he would deliver Arnold. But his plan miscarried owing to the fact that Arnold moved his headquarters to another part of the city. For a long time Champe endured many hardships, and was unable to escape and return to his comrades until serving under Lord Cornwallis at Petersburgh, Virginia.

The Old Tuers Homestead.
The English evacuated Paulus Hook November 22, 1783. It is said that during the Revolution there were only fourteen families in Bergen whose sympathies were with the Colonies. Among these were some very devoted patriots whose memory should be cherished. Prominent among them are the names of Mrs. Jane Van Reypen Tuers and her brother Daniel Van Reypen. Mrs. Tuers lived at the old Tuers house, the site of which is now occupied by the Armory on the corner of Mercer street and Bergen avenue. During the time the British occupied New York the American prisoners in their hands suffered for food and Mrs. Tuers carried to them sacks of provisions every week. From the weight of the heavy burthens she injured her shoulder and arm so seriously that she was crippled for the remainder of her life.
Upon these occasions she used to go to "Black Sam's" Tavern, which was a rendezvous for the English officers. One day, under pledges to not reveal the source of her information, Black Sam told her that he had overheard British officers talking of a conspiracy in the American Camp. She told her brother, Daniel Van Reypen, who went to Hackensack ostensibly to visit relatives; he saw General Wayne, and saying that he could trust him, advised him to mark every tent in the camp as there was a conspiracy. General Wayne sent the warning to Washington; thus was Arnold's treason learned three days before the capture of Andre. Gen[Pg 62]eral Washington offered Mr. Van Reypen a reward in money to which he replied, "No, I do not serve my country for money; but in case I am taken prisoner by the English I would like to be released," upon which Washington said "that the best hostages should be given for him." Mr. Van Reypen built and lived in the house still standing on Fairmount avenue, No. 320, a little west from Bergen avenue. Mrs. Tuers died in 1834, and her remains lie in an unmarked grave in lot 136 of the cemetery on Bergen avenue, east of the church.
General Bayard, who owned an estate at Hoboken called Castile—since known as Castle Point—was at one time friendly to the Americans, but later he became a very pronounced Tory and very vindictive towards all who sympathized with them. At one time Mr. Daniel Van Reypen was arrested and taken before him, when General Bayard greeted him with the question, "Old man, where is your rebel coat?" Mr. Van Reypen responded, "The coat does not make the man, it is the heart." Later, Mr. Van Reypen met General Bayard in New York, near the river, when General Bayard threatened to strike him with his riding whip, to which Mr. Van Reypen coolly replied that if he did, he would throw him off the dock, and the angry General passed on.
Another sister of Mr. Van Reypen's had an amusing encounter with a loyalist friend, a Mrs. Outhout, who was constantly assuring her that the rebels would be defeated and that "there would be a devil of a stroke very soon." When Cornwallis surrendered, Mrs. Van Horn quietly reminded her of her prophesies and asked "if this was the stroke?"
Catherine Van Winkle and her younger sister Maria were very heroic girls whose names should not be forgotten. They often carried messages from Lafayette to Washington at Belleville; on one occasion they walked there in the night to warn Washington of a plot of the English to surround and capture him. To their quick wit an American soldier owned his life. He was at their father's house, an old stone house a little south of Colonel Spier's burying ground, near where Highland and Idaho avenues now cross, when a party of English soldiers surrounded the house in search of him. The girls hid him between the feather and straw beds of their bed, and then retired, and when the English entered the room to search for him were seemingly sound asleep. The English prodded with their bayonets under the bed and searched every closet and corner but failed to find him. Catherine married a Mr. Sheppard and was a well-known and beloved character on the Hill until comparatively recent times; born in June, 1763, she lived to be one hundred years and six months old, and was bright, cheerful and active to the last. Her remains lie in an unmarked grave in the cemetery opposite the Dutch Reformed Church. Washington appreciated the loyalty of the family and was a guest of their father's, sometimes dining there. One branch of the Van Winkle family still have in their possession a handkerchief left by Washington upon an occasion of his staying over night at the Stuyvesant Tavern.
It is to be regretted that so much has been forgotten of the early customs and habits of former generations of this locality. For a long time the city grew slowly; in comparatively recent times the farms have been changed into city lots and the occupations and amusements have taken different forms. Even traditions of early customs does not reach much farther back than the beginning of the present century; but, owing to the Dutch tenacity of clinging to inherited customs, it is probable that the manners of eighty and a hundred years ago were not so very different from those of their ancestors, especially as they retained the quiet, simple life of a farming community. The great holiday of the year, looked forward to alike by the old people, young men and maidens and the children, was New Year's Day. Christmas was observed by a service at the church, and not by gifts and friendly reunions; all the jollity was reserved for New Year's day. Then the mother or the grandmother brought out the bag of Spanish silver dollars, and each child was allowed to take out one as a New Year's gift. In every house was a store of "oley koecks" and New Year's cakes, a sort of "jumble" or cookey, in shape either oblong or round, stamped with a design of a vine, or bird, or flower, from a wooden stamp; these were kept ready to give to the bands of visiting children who went from house to house wishing the inmates a "Happy New Year." The young people went for long sleighrides to[Pg 65] neighboring towns, or friendly calls; the older people made visits in the evening, dropping in upon their friends without an invitation and staying to supper. After the New Year's festivities, the "quilting parties" were the favorite social entertainment, when the young women spent the afternoon in quilting the elaborate patch work or other quilts; some were made of homespun woolen cloth and instead of cotton, wool was used as a filling, and the quilting was in most elaborate designs of vines and flowers. The young men came to supper and the evening was spent in games and dancing. Then came the "Husking bees" in the fall, varied by occasional "Apple-paring bees," but the latter were more unusual. The women made occasional afternoon visits, guests coming soon after the mid-day dinner and staying to tea.
The great day among the men came in June at the general muster of the militia, or "General Training Day." This dated from the early days of Bergen, the first militia having been organized June 30th, 1663. All men between eighteen and forty-five (or fifty) years of age were required to meet upon that day each year to go through military evolutions. All who absented themselves without a valid excuse were subject to a fine. There was a company at Hackensack, one at New Durham, one at Bergen and another at Bergen Point. The several companies of the county formed a brigade and met at different places on successive years, more frequently at New Durham or Bergen. Colonel Sip was a colonel of militia and John I. Van Horn a captain. Both served in the war of 1812-14. Captain Van Horn was in charge of a rough block fort at[Pg 66] Sandy Hook. He used to say that there was nothing to do only when an American ship was being chased by the enemy, their guns afforded it protection and enabled it to get safely into port. The war of 1812-14 being largely a naval war, the militia of this locality did not take a very active part in it. But during the war, the fort at Paulus Hook was held by Drum Major John G. Sexton of the militia and six men under his command. One great enjoyment of "Training Day" with the Bergen Company was the supper they always had at the tavern on Bergen avenue. This supper was a great event, looked forward to through many months. While all meals at this tavern were held in high esteem, upon this one day there was an unusually fine menu. The praises of those gastronomic successes are still sung by such of the fortunate participants as are still with us.
One peculiar custom among the Bergen Dutch, handed down from generations even to recent times, has been that the masculine head of the family always cut the smoked beef (a never failing dish) and the bread. Formerly the bread was baked in large loaves in yellow earthen dishes in a brick oven, and put upon the table uncut, then as each person wished a slice the head of the house, holding the bread against his breast, cut off a portion. Generally they lived very plainly; sauerkraut, which was such a favorite dish among the Mohawk Valley and Albany Dutch, seems to have been almost unknown here. Pound cake was a favorite recipe and in the early part of this century the Communipaw housewives carried their butter and eggs to certain bakers in Greenwich street, New York, to have their pound cake baked for them. Their recipe for[Pg 67] crullers was very similar with the addition of a little more flour. In all well regulated houses "Oley Koecks" were indispensable; there was quite a difference in the way of making them, some recipes are plain doughnuts of raised bread dough, sweetened and spiced only. The following is a more elaborate recipe of 1750:
"One pint of milk, one cup fresh yeast, flour to make a stiff batter, mix at night; in the morning add five eggs, two cups of sugar, one cup of shortening, (half butter and half lard), one teaspoonful soda, flour to make like bread dough, let stand until light, which will be two or three hours; have ready chopped apples sweetened and flavored with nutmeg and raisins; roll out and cut in pieces about four inches square, place a tablespoonful of apple on each square, double over and pinch together, drop in hot lard to fry."
In the old recipes pearlash is used, in these the modern term soda and baking powder have been substituted. The early settlers made their own pearlash by burning either corn cobs or a bit of wood, often birch or maple, on the hearth, and from the clean ashes put in water obtained the carbonate of potash desired.
The following recipes are also handed down from the early Dutch housewives:
"Jumbles, (Koeckjes): One pound of flour, one half pound of sugar, less than half pound of butter, three eggs, four tablespoons sweet milk, one teaspoon saleratus."
"Dried Biscuits, (Old Dutch): Take one and a half pints warm milk, one cake compressed yeast, one teaspoonful salt and flour enough to make a sponge.[Pg 68] When light, which will probably be in half an hour, add one-fourth pound of butter, and knead with flour to about the consistency of bread. Let rise again and then mould each biscuit in two parts, putting one on the top of another, that they may be broken open more easily. Put in pans and let rise before baking. When baked break open and put in the warming oven until thoroughly dried."
"Soft Waffles, (Old Dutch): One quart of milk, make a batter with flour, raise with yeast, when light add four eggs, one-quarter pound of melted butter and a little salt. Beat all together, let rise again, and add half a cup of sugar. Eat with sauce."
Old waffle irons with initials of early owners and the date are still in existence; one has A. D. 1709.
"Fried Spack and Opples: Take slices of pickled pork, fry them well, then take slices of apple and fry in the hot fat; if the apples are sour, put a little molasses or brown sugar over them, when the apples are brown, turn over and brown on the other side; serve with the slices of pork laid around the edge of dish. If the apples are sweet, do not use sweetening."
"Mince Pie, (Old Dutch): Seven bowls chopped tart apples, three bowls chopped meat, seven pounds of sugar, one gallon cider (not sweet), seven nutmegs, four tablespoonsful cinnamon, two tablespoonsful cloves, two pounds of raisins, one pound of currants, one pound of citron, salt and pepper."
"Buling Pudding, (Old Dutch): Four quarts of water, let it come to a boil. Add one pint of rice, two cups of sugar, one-fourth pound of cinnamon, one tablespoonful of salt, and buckwheat enough to make a very[Pg 69] stiff batter. Boil half an hour. Put in pie dishes and when cold cut in slices and fry."
"Buckwheat Pudding, (Old Dutch): Have one quart of water boiling. Mix two cups of buckwheat meal to a smooth batter with cold water; stir this mixture into the boiling water; add to this one slice of raw, fat salt pork chopped fine, one cupful of sugar, one teaspoonful each of ground cloves, allspice, cinnamon and salt. Simmer one hour, stirring frequently. Pour into a deep dish to cool. When cool this will leave the dish easily if sufficiently cooked. Slice, fry brown and serve with powdered sugar."
These two puddings recipes are still used in Holland.
Cookstoves were not introduced until about 1825 or later, the cooking being done over an open fire. In the wide fire-place was fastened at one side the "crane," a swinging iron bar, on which were hung iron pot hooks, or trammels, upon these were swung the pots and kettles for cooking. These were cleaned from soot and smoke by rubbing them in the sand. The fire was built with a large log for back log, resting on andirons, and in front and above it were piled smaller sticks and chips of wood. They used kettles of different sizes made with three iron feet, long handled frying pans; bake kettles—broad, shallow kettles with iron covers upon which hot coals were piled; skillets, a small iron pot, holding from one to two quarts, with short handles and three iron feet, to set on a bed of coals in front of the fire to cook little messes. Meats were roasted suspended by a string before the fire and twirled from time to time, or in tin Dutch ovens, which were open towards the fire. Bread, cake, etc., were baked in the[Pg 70] brick oven. The ordinary bread used was of rye and Indian meal. The brick ovens were prepared for baking by building a hot fire in them and when the wood was burned to coals it was shovelled out and the bread, etc., put in and the oven securely closed. A long handled shovel called a "peel" or a "slice" was used to put the things in to bake. Beside the fire-place stood shovel and tongs, and usually there hung there a bellows for blowing up the fire when low, and a turkey's wing to brush up the hearth. The first stoves used were the Franklin and many of those used in Bergen were cast by Martin Ryerson at Pompton, N. J. Coal was not used for fuel until about 1826, and at first in grates only.
The killing of their own beeves and pork was practiced by the farmers of Bergen and Communipaw as late or later than 1840. They lived almost entirely upon the produce of their farms. In November they killed and laid up their year's supply of meat. The skins of the beeves were sent to the tanner who cured them for the half; from their share the boots and shoes for the family were made by a shoemaker who came to the house to work. This custom was kept up until 1825.
In the early days there were large tracts of white cedar along the western slope of Bergen Hill, on the old swamp road to Belleville which led from the Newark Turnpike and near Sikakes. From this cedar the farmers had casks made in which to keep their salted meats. Fresh meats, sausages, in immense quantities, head-cheese, and "roellachoje" (a pickled preparation of beef tongue and tripe) were kept in a cool garret. The[Pg 71] first butcher in Jersey City was John W. Holmes, who started about 1814; he was succeeded in 1816 by Henry Drayton, who came to Jersey City from Somersetshire, England, but city ways and conveniences did not reach Bergen and Communipaw for many years later. It is said that the first huckster known in Jersey City was a character called "High, Low, Jack," who, in the '60's, began to go about from house to house selling clams and huckleberries. His cries were a constant amusement to the children, who used to follow him in crowds.
During the first quarter of this century, wool from their sheep was spun and wove at home; the spinning was done by the women of the family, sometimes assisted by young women who "went out spinning." Men went about to do the weaving. On some places there were weave houses, in others there was a weave room in the cellar. When the cloth was woven it was usually dyed blue; a blue dye tub being kept to dye the stocking yarn and cloth. Later the cloth was sent to the fullers, then tailoresses came to the house and made it up into clothing for both men and women.
The women went to New York to market, carrying butter and eggs to sell, and there are traditions in some families of their avoiding the "Mill and Church road" on their return, and climbing over the rocks, in the long walk from the ferry, fearing that they might be robbed of their store of silver dollars, carried in the large pocket, fastened about the waist and worn under the dress skirt. A story is told of a very philosophic old lady who sold buttermilk which her customers accused her of diluting with water. The proceeds she[Pg 72] invested in a silver tankard. Upon her return from New York in a row-boat across the river, it was so rough that in the rocking of the boat the parcel with the tankard fell overboard and was lost. "Well," exclaimed the old lady, "let it go, it came from the water and has gone back to the water."
A great event to the children was the yearly candle-making in many families; they were all allowed to make a few little candles for themselves when they were so fortunate as to be the happy possessors of toy candlesticks. Candle-making was quite a long and wearisome process. First the proper length of candle wicking was doubled over long slender rods, and the ends twisted together to form the wick of the prospective candle. The number of these upon a rod depended upon the size of the candle to be made, whether six or eight to the pound. These were prepared the day before the dipping was done. In the early morning long pieces of scantling were laid upon two saw-horses, and across these scantlings were laid the rods with the wicks hanging down. At one side was placed a large "cauldron kettle" filled with hot melted tallow into which the operator dipped the rods of wicks. The kettle of hot tallow was kept replenished and the dipping process was repeated again and again until the candles were of the required size. After being properly cooled they were slipped from the rods, the wicks cut off and they were carefully packed away in boxes. Later candle moulds were invented, which made it very much easier than the old method.
In dress the women did not wear the ornamental caps, such as were worn in Holland, but very plain[Pg 73] ones; neither did they wear as many petticoats as their sisters across the sea, three or four usually being the limit. It was not the custom here in Bergen, to set apart a dower chest for each daughter, to which yearly additions were made of household and personal linen, and a silver spoon, as was practiced by some of the Holland families in Albany and in some parts of Pennsylvania. Upon marriage each daughter was given a little store of linen; upon the death of her father, perhaps a little money; but, as a delightful old lady told me, "the land and the property mostly went to the sons, the girls were expected to marry money." Under the old Dutch law both sons and daughters became of legal age at twenty-five. The girls were carefully trained in household arts and in the use of the needle. Little girls under nine years of age wrought elaborate samplers. It was a common practice to make the pillow cases with an insertion of drawn work in linen at the closed end of the case, under which showed the bit of red cloth sewed on the end of the pillow; the open end of the pillow case was left untrimmed.
Children were taught to be very courteous to their elders; upon meeting any one in the street little girls curtesied and the boys made a bow. The Bergen Dutch women and their daughters were very practical thrifty women, most excellent housewives and devoted mothers. Both men and women devoted themselves in the most matter of fact way to the duties of life, never allowing anything less serious than a funeral to disturb to any great extent the routine of daily life. I have heard of a bride brought home upon her wedding day to her father-in-law's house, who, upon the first evening[Pg 74] started out to milk the cows, saying she "preferred to take up the duties of her new position at once." I have heard also of a bridegroom, a merchant who attended to his usual duties upon the morning of his wedding day, and after the ceremony returned again to his store.
Slavery existed until 1820, when all slaves were made free at twenty-five years of age. The old slaves were cared for during the remainder of their lives. It was for the colored people that the first Sunday School in Bergen was opened in 1828, in the garret of the school-house. Many of the slaves ran away to New York and Connecticut. Those who went to New York lived in cellars or wherever they could find shelter. When any of them died their friends always brought them back to Communipaw to bury them, and their funerals were held at the old Garrabrant stone house, which used to stand on what is now Philip street. One peculiar feature was that on every coffin was placed a bunch of freshly plucked spearmint. They were buried on the Garrabrant farm in what is now Lafayette, and also on the Van Reypen place.
A hundred years ago, lotteries were held in great esteem, as a popular means of raising funds to build churches, colleges, schools, roads, prisons, and charitable institutions. The first ever drawn in this locality was at Paulus Hook in 1773, and in 1824 a "Queen's College Literature Lottery" was advertised in Jersey City. Some of Jersey City's most reputable people were engaged in lotteries and accumulated fortunes in the business. Later the Legislature passed laws making it illegal and the parties then conducting a lottery in Jersey City removed their business to Wilmington, Delaware, where it was carried on for many years.

A. Dey, Jacob Radcliff, Rich. Varick
Paulus Hook with its ferry rights passed from the possession of the Van Vorst family to Anthony Dey of New York, on March 26th, 1804. The consideration was an annuity of $6,000 in Spanish milled dollars. Dey conveyed it to Abraham Varick, who on the 20th of the same month conveyed it to Richard Varick, Jacob Radcliff, and Anthony Dey. These men were eminent and successful lawyers in New York and became the founders of Jersey City. They divided their purchase into one thousand shares, associating others with themselves. A map of the property was issued and a sale of lots was advertised for May 15th, then adjourned to June 12th, 13th and 14th. Upon the 10th of November, 1804, the Legislature passed an act incorporating the "Associates of the Jersey Company." This bill was drawn up by Alexander Hamilton. To this corporate body Radcliff and Dey conveyed Paulus Hook, February 1st, 1805. For fifteen years the Associates possessed the government and shaped the destinies of the town and their influence lasted long after the original members of the company were all dead. The corporation still exists and owns much valuable property.
At various times the city limits have been extended, and various acts of Legislature have changed the governing power. In 1820 the Legislature passed an "Act to Incorporate the City of Jersey, in the County of[Pg 76] Bergen." On the 23d of January, 1829, the corporate name was changed to "The Board of Selectmen and Inhabitants of Jersey City." On February 22d, 1838, the governing power was vested in the "Mayor and Common Council of Jersey City." It now ceased to be a part of Bergen Township and became a separate municipality. Dudley S. Gregory was the first Mayor of Jersey City. He served in that capacity in 1838-'39-'41-'58 and '59. He lived in the building now used as a post office on Washington street, in what is still a pretty part of the city, with its four park corners on Washington and Grand streets. Mr. Gregory was a man of wealth and of public spirit; he imported a large number of European shade trees, among them the variety of "horse chestnut" which has become a favorite shade tree throughout our eastern states, to such an extent that our native horse chestnuts or buckeyes are scarcely known in the east, the principal difference being that the native varieties have smaller clusters of flowers which shade from a yellow or pink tinge to a deep pink or dull red. On March 8th, 1839, the city boundaries were extended along the northerly side of First street to the center of Grove street, thence southerly into Communipaw Bay to the line of South street, extended. Hudson County was set off from Bergen County in 1840. The township of Van Vorst, founded in 1804 by John B. Coles, was separated from the township of Bergen, March 11, 1841; it included all that portion formerly known as Ahasimus. In March, 1851, it became a part of Jersey City.
In 1869 there was an effort made for the consolidation of the several cities and townships in Hudson[Pg 77] County, east of the Hackensack river, into one under the name of Jersey City. At the election held October 5th, 1869, Jersey City, Bergen and Hudson City became one. The latter had been taken from the township of North Bergen and incorporated as the "Town of Hudson in the County of Hudson" on March 4th, 1852. On the 11th of April, 1859, it was incorporated as the "City of Hudson," with powers of government vested in a mayor and common council. In 1873 the town of Greenville was annexed to Jersey City by legislative act. Greenville was originally a settlement of German families on a part of the Gautier tract. Lafayette was never a separate municipality; the name was given by a land company to the Garrabrant farm when it was bought and mapped out in town lots in 1856. The lots did not sell well until after the war.
Paulus Hook and Van Vorst.
In the map of the new city prepared by the Associates, the streets were laid out at right angles and one thousand three hundred and forty-four lots were laid down. The eastern boundary was Hudson street, which was laid in the water with the exception of a small piece of upland that extended outward at Morris street. The southern boundary was South street, later called Mason street, and a few years ago vacated by the city. Harsimus was the northern boundary. It was nearly circular upland, of which the greatest extent was from one hundred feet north of Montgomery street to one hundred and seventy-five feet south of Essex street. More than half of the site for the proposed city was marsh and land under water. The westerly boundary was a line drawn from the east side of South street to[Pg 78] a point near the corner of First and Washington streets. It was the plan of the Associates that the western border should front on a tide water canal, an island city, bordered by piers and docks and surrounded by navigable water. The Jersey City Journal's History of Jersey City claims that the city has lost commercial prestige by the failure to carry out that idea, also that another and even greater blunder was committed by the filling in of Mill Creek, which had been navigable by small sloops. The new city met with many discouragements; New York claimed jurisdiction over all lands under water up to low water mark on the Jersey shore. Alexander Hamilton and Joseph Ogden Hoffman, as counsel to the Associates, gave a guarded answer that New York had no right to land under water at Paulus Hook. This boundary dispute was not settled until 1889. Mr. Van Vorst would not accept an equivalent for the annuity, which affected deeds and prevented many from purchasing the lots.
In March, 1804, Colonel John Stevens, who had bought the confiscated estate of William Bayard, known as Castile, founded the city of Hoboken. One of the first measures was to build a road to Hackensack and to the Five Corners to bring travel from the different villages to his ferry. In December, 1804, the Associates organized the Newark Turnpike Company, which built the road now known as Newark avenue from Warren street to the Hackensack river. Through lower Jersey City it was a macademized road through a marsh. Previous to this there were but three roads in Harsimus—one the causeway leading to Paulus Hook now known as Newark avenue, second "the road to church[Pg 79] and mill." This followed what is now the line of Henderson street, along the shore of Harsimus Cove to First street, where a bend carried it to the corner of Grove street and Newark avenue; thence it followed the present line of Newark avenue to Monmouth street, along the foot of a sand hill which was the site of an earthwork outpost erected by the British during the Revolution. The last vestige of this hill, at the corner of Mercer and Brunswick streets, was removed in 1894. From this hill, nearly on the line of Railroad avenue, the road ran to Prior's Mill on Mill Creek just below the Point of Rocks, thence by what is now Academy street to the village of Bergen. The third road began near the Van Vorst house on Henderson street and ran northwesterly to a point where Jersey avenue and Second street now intersect; thence at an angle to the base of Bergen Hill, where it crossed the road built by Stevens to Hackensack.
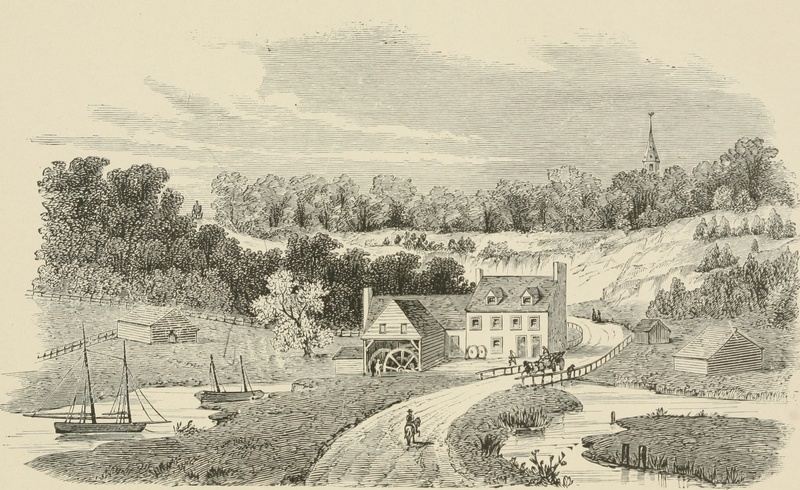

Prior's Mill.
The Associates built several little piers and a retaining wall along the east side of Hudson street from Grand to Essex, which served as a wharf for light draught vessels. They partly graded several streets and set out along them some six hundred shade trees, among them some Lombardy poplars, of which almost the only survivor is, or was recently, still standing near Mills' Oakum works on Wayne street. Lombardy poplars were introduced into this country by Andre Michaux, a French botanist, who came here in 1786 with letters from Lafayette to Washington. He was authorized by the New Jersey Legislature to acquire an alien's title to two hundred acres of land and to "establish a Botanical Garden at Bergen." His place[Pg 80] was known as the "Frenchman's Garden," and is now included in the "Macpelah Cemetery." The Associates reserved land for churches, a school, a shipyard and a public market. They urged Robert Fulton to establish his works in Jersey City and sold to him a block of ground for $1,000 on five years time without interest. The deed was dated November 3d, 1804. His foundry was on the corner of Green and Morgan streets, with a dry dock in front of it; here he built his first machinery for propelling a vessel by steam. The first steam boilers were of copper and wood was used for fuel.
In 1804 Joseph Lyon, of Elizabethport, leased the ferry and moved the landing and stairs about midway between Grand and York streets, the slip opening diagonally up the river. There were two row-boats with two oarsmen each and extra oars for the passengers to use if they were in haste to cross, and two periaugers. In 1805 the Associates built a new tavern of brick, known as the Hudson House. It is still standing on Grand near Hudson street, and is part of the Colgate Soap works. Between this hotel and the ferry landing was a semi-circular plot around which the stages would run to unload their passengers. In the center of this plot was a willow tree which was sometimes used as a whipping post. Winfield tells that as late as 1814 a white-headed old man here received thirty-two lashes. The newspapers of the day advertised over twenty daily stage lines, besides the irregular stages, communicating with all parts of the state, and farmers wagons, even from Pennsylvania, brought produce to New York by way of this ferry. Horses and wagons were lifted on to the sail boats, but the ferriage was so expensive that in general the produce and freight was put upon the boats and the teams and wagons left in the stables of the Hudson House. The ferry site has been frequently changed. Its second removal was to the foot of York street; on April 1st, 1839, it was changed to the corner of Montgomery and Hudson streets; in 1856 the block east of Hudson street was filled in and the landing was changed to its present location.
In the fall of 1809 several Newark gentlemen subscribed $50,000 to start steam ferryboats, and Fulton was asked to construct such a boat as he would consider suitable for the purpose. In March, 1811, they obtained the lease of the ferry and the right of landing on the New York side. Two boats were built by Charles Brown, a noted ship-builder of New York, who had built the Clermont in 1807 for Fulton, and whose shipyard was on East river near Fourth and Sixth streets. They were eighty feet in length and thirty feet in width. The boats were named the Jersey and the York. The Jersey was the first boat finished and began her regular trips on July 17th, 1812. A passenger on its first day wrote to the "Centinel of Freedom," "I crossed the North river yesterday in the steamboat with my family in my carriage, without alighting therefrom, in fourteen minutes, with an immense crowd of passengers. I cannot express to you how much the public mind appeared to be gratified at finding so large and so safe a machine going so well. On both shores were thousands of people viewing this pleasing object." There was a grand entertainment to celebrate the occasion given at Lyons Tavern, to the Mayor and Common Council of New York and others.
I give Fulton's description of the boats as quoted by Winfield in his History of Hudson County: "She is built of two boats, each ten feet beam, 80 feet long and five feet deep in the hold; which boats are distant from each other ten feet, confined by strong transverse beam knees and diagonal traces, forming a deck thirty feet wide and eighty feet long. The propelling water wheel is placed between the boats to prevent it from[Pg 83] injury from ice and shocks on entering or approaching the dock. The whole of the machinery being placed between the two boats leaves ten feet on the deck of each boat for carriages, horses and cattle, etc.; the other having neat benches and covered with an awning, is for passengers, and there is also a passage and stairway to a neat cabin, which is fifty feet long and five feet clear from the floor to the beams, furnished with benches and provided with a stove in the winter. Although the two boats and space between them give thirty feet beam, yet they present sharp bows to the water and have only the resistance in the water of one boat of twenty feet beam. Both ends being alike and each having a rudder she never puts about.
The Plan of the Jersey.
"The dock is one hundred and eighty feet long and seventy feet wide, the bridge is fastened to the middle of the bulkhead. The boat being only thirty feet wide and the dock seventy, leaves twenty feet vacant on each of her sides; in each of these twenty feet spans and in the water are floating stages, made of pine logs, which lie favorably to the boat for thirty feet, and these run diagonally to the extreme end of the wharves, so that the boat when coming in hits within the seventy feet and the stages guide her direct to the bridge."
In 1813 the York, built on the model of the Jersey, was completed and placed on the ferry. It is said that "they ordinarily took an hour and a half to make a trip." They started at sunrise from each side of the river and ran all day, every half hour, by "St. Paul's Church clock." The fares were collected on the boat during the passage over. The Jersey was in service for many years and finally being condemned, was[Pg 84] broken up and sold to Mr. Isaac Edge, who built a stable from its planks and beams. From a portion of this wood two canes were made, which are still treasured in the Edge family.
The Ferry Company had a very unfortunate experience; they sank all of their capital and in 1824 were obliged to assign their lease to Francis B. Ogden, Cadawalder D. Colden, and Samuel Swartout, who secured a new lease for fifteen years and six months from November 1st, 1825. They were to provide two good steamboats, but were afterwards permitted to use a team-boat in place of one. They were also to provide row boats. They bought and placed on the ferry the Washington. Within a year Messrs. Ogden and Swartout transferred their interest to Mr. Colden; he failed to make it remunerative and surrendered the lease to the owners, "the Associates of the Jersey Company." January 1st, 1831, they leased it to the New Jersey Railroad and Transportation Company. By renewals the lease was continued until 1853, when the Railroad bought up the stock of the Associates and became the owners of the ferry. The first night boat was put on in June, 1835. The line to the foot of Desbrosses street was started in 1862. These ferries were transferred to the Pennsylvania Railroad Company in 1871. Among the various schemes to secure patronage for the ferry by bringing people from New York, was the erection in 1825 of a large amphitheatre on the south side of Sussex street, between Hudson and Green streets, on land leased from Mr. Drayton, Sr. For about two months large numbers, mostly from New York, gathered here on Fridays to witness the fighting of bulls, bears, buffaloes and dogs.

The Edge Windmill.
A quaint and interesting landmark of lower Jersey City, for some thirty years, was the windmill near the corner of Montgomery and Green streets; to be exact, it stood upon a pier one hundred feet in length, seventy-five feet north of Montgomery street, and fifty feet east of Green street. According to the family traditions this mill, an exact duplicate of one owned by himself in Derbyshire, England, was sent by Mr. Edge, Sr., to his son Mr. Isaac Edge, soon after he settled in Jersey City in 1806, in appreciation of his success in the New World. Every part was marked to insure its proper erection. The motive power was a windmill upon an octagonal stone tower seven stories in height. The fans on the wings were originally of canvas, but these were destroyed by a September gale in 1821, when Mr. Edge replaced them with iron fans. It was quite a celebrated mill and considered the best in America. It faithfully ground its grists until taken down in 1839 to make room for the New Jersey Railroad tracks; but its days of usefulness were not over, it was removed to Town Harbor, L. I., from there it was taken to Southold, L. I., where it continued to do good work until destroyed by fire on June 25th, 1870.
In connection with the mill Mr. Edge started a bakery, which not only supplied Jersey City people with their daily bread at twenty-five cents a loaf, but ships also. The bakery stood on the southwest corner of York and Green streets. It was burned in 1811,[Pg 86] but Mr. Edge rebuilt it and the building is still standing. The family still have in their possession the ledger of the old mill and some of the entries are very interesting. The accounts were kept in English currency until 1816. In 1812 flour was sold at the mill for eighteen dollars per barrel. Abraham Reynolds paid one pound, sixteen shillings to have forty-five bushels of wheat ground and three shillings and six pence for its ferriage across the river. The freight on three barrels of bread sent to Sandy Hook was four pounds, four shillings, three pence. James Parker received for his labor only five shillings a day, while Jabez Spinning received thirteen shillings. Mr. Edge lived at the corner of Green and York streets on the water front.

Town Hall and School
The first school on Paulus Hook was started in 1806. The Associates gave the land and the town authorities provided the money for the building, which was located on the two lots east of St. Mathew's Church. The building was used also as a town hall and a meeting place for the different religious denominations. The school was called the "Mechanics' Institute" and was a pay school. Soon after the "Columbia Public School" was started and supported by subscriptions. In 1834 both failed financially and were combined and reorganized in 1835 as the Mechanics' School. In 1838 the mayor and common council, under the new charter, removed the building to the rear lot and remodeled it as a school-house, town hall and jail, at the cost of $1,300. After a time the building used as town hall, church, school and jail ceased to be used by the city officials, who met at different taverns and halls until 1861, when the city hall was completed at a cost of $135,145. It was situated on the south side of Newark avenue west of Coopers' alley. The council chamber was artistically frescoed by a brother of General Garibaldi, then a refugee here. The wall behind the president's desk represented a Venetian scene from a columned piazza, and was dainty and effective. Some years later it was ruined by a house painter in repairing and renovating the room. In 1887, measures were begun to erect a larger city hall to meet the demands of the larger city. The corner stone of the new building was laid at noon[Pg 88] May 26th, 1894, and it was completed January 1st, 1896. It is located on the block between Grove and Henderson, Mercer and Montgomery streets. The total cost, $736,267.56. It is quite an imposing building and large enough to accommodate the various departments of the city government. The interior arrangement is particularly fine; upon entering, the broad corridors give a pleasant impression, and the offices are spacious, light and commodious. An attempt is being made to have in the mayor's room, portraits of the mayors of Jersey City. Several have been presented but the list is not yet complete.
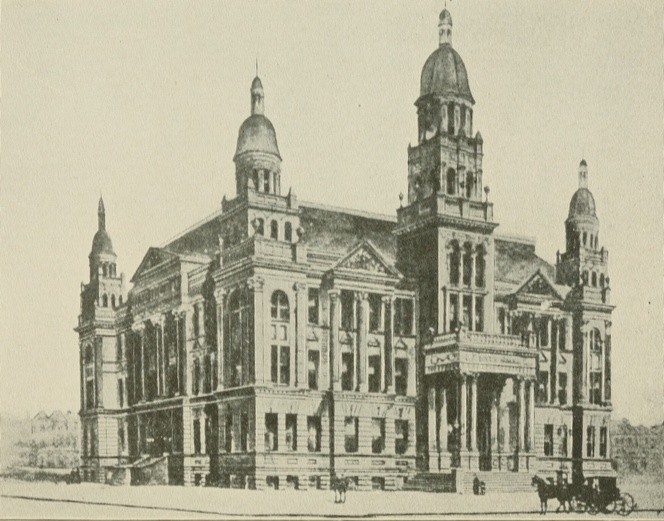

New City Hall, Jersey City.
In 1843 the state school money, the receipts from liquor licenses and the money received from the Bergen Township funds were appropriated for the Public School, then first called School No. 1. It was still held in the Town House. The primary pupils paid fifty cents a quarter, in the higher branches the fees were one dollar a quarter. Where the pupils were unable to pay, their dues were charged against the public funds. In 1847 a new school house was erected in York street, west of Washington street. It still forms the central portion of the present school building which has just been remodeled and rebuilt, and is now a very beautiful structure. In 1848 the school was opened with Mr. Linsley as principal, who is said to have organized at School No. 1 "the first Normal School in the country," possibly in this state, but in 1840 there was a Normal School at Camden, Oneida County, New York.
In 1846 Columbia College presented Jersey City with a free Scholarship, which was accepted by the Common Council on March 26th, 1847. Several students from Jersey City had the benefit of this scholarship as late as 1890, about which time the privilege seems to have been withdrawn. At present a free scholarship in the University of the City of New York and one in Rutgers College are open to the young men of Jersey City who attend the High School. The only condition being that the applicant must attain a certain percentage and stand in the upper third of the graduating class. The next vacancies will occur in June, 1899, In 1860 Mr. William Dickinson became a member of the School Board and practically reorganized the school system. Until his death he was connected with the Board in some capacity and to him is due in a large degree the excellence and the high standing of the Jersey City schools. The High School was organized in 1872 and in 1876 stood second only to the Boston High School.
In her various public schools, Jersey City possesses a splendid corps of teachers, whose faithful, efficient work has been broadly demonstrated in the practical education of hundreds of men and women of Jersey City. The many who have been able to have more extended educational advantages look back with pride to their early school days in Jersey City's public schools, where were laid the thorough foundations of their education. In 1897 the Women's Club started a free kindergarten; in 1898 the Board of Education[Pg 90] came to their assistance, and before very long we hope to see the kindergarten a recognized branch of the public school system of our city. There are many private and parochial schools of great excellence in the city, but this is too limited a sketch to do them justice.
The first post office was established in Jersey City in 1807 by Postmaster General Grainger. Up to that time people went to New York or Newark for their letters. For many years people called at the office for their mail; then there was a local system of carriers, people duly authorized who delivered letters at the houses, for which they received one cent on each letter, the only pay allowed them. This method was in operation as late as 1867, possibly later, but about that time carriers were appointed and paid by the government. Sub-stations were started after the consolidation of the cities. The lamp post boxes came somewhat later. I am told that there was no post office in Bergen until the establishment of a sub-station. After the consolidation of the cities, newspapers were sent from the Newark or Jersey City office to a store in Bergen. Just when the Hudson City post office was opened I cannot say, but during the Civil War the Bergen people came to Hudson City for their mail.
The Bergen Church had made an effort to start a branch at Jersey City, but the first successful church society was that of St. Mathew's Episcopal Church which was organized August 21, 1808. The services were held for several years in the school building. October 22, 1831, the corner stone of the church was laid on Sussex, between Washington and Warren streets; the building was consecrated November 26, 1835. The first Presbyterian society in Jersey City was founded in 1809 and held services in the Jersey Academy. The first Presbyterian Church was organized December 15th, 1825. The Particular Baptist Church of Jersey City and Harsimus was organized March 11, 1839. The building is still standing on the west side of Barrow street, between Newark and Railroad avenues. Trinity Methodist Episcopal Church was organized in 1836. It is said that the first Catholic services in Jersey City were held for the French potters that were brought over to make porcelain, but the Roman Catholics of New Jersey were under the jurisdiction of the diocese of New York until October 30th, 1853, when the diocese of New Jersey was created. St. Peter's Roman Catholic Church, begun in 1831, opened for service in 1837, stood on the site now occupied by St. Aloysius Academy. The second and present building is on the northeast corner of Grand and Van Vorst streets. This parish has been in possession of the Jesuit Fathers since April 13, 1871. The[Pg 93] Tabernacle Church, the first successful Congregational Church in Jersey City, was organized in 1858; it is situated on the southeast corner of Henderson and York streets and is noted among other things for its "People's Palace" and good work among the poor of the parish. From 1853 until 1859 there was an Unitarian church on the southeast corner of Grove and Montgomery streets. The pastor, Rev. O. B. Frothingham, was a very talented man and popular lecturer, but soon after he left the society disbanded. As early as 1852 attempts were made to organize an Universalist Church, but none were successful until 1872, when the First Universalist Church of Jersey City was incorporated. There are now nearly one hundred churches of the various denominations in the city.
1824 saw the opening of Dummer's Glass Works on Communipaw Cove, west of Washington street and south of Morris Canal. The site is now occupied by the sugar house. The flint glass of these works, started in 1824, has never been excelled. In 1825 the Jersey Porcelain and Earthen Ware Company was incorporated in the Town of Jersey, County of Bergen. Under the Act of Legislature George Dummer, Timothy Dewey, Henry Post, Jr., William W. Shirley and Robert Abbatt, Jr., were named as incorporators. In 1826, at the exhibition of the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia, a silver medal was awarded to this pottery for the "best china from American materials." This pottery is exceedingly interesting from the fact that it was the pioneer in America along several lines; it was the first to manufacture porcelain, for which French workmen had been brought over. For three years they manufactured porcelain of good body and excellent glaze. About 1829 Messrs. D. and J. Henderson bought the works and manufactured flint stone ware of superior quality.
In 1833 David Henderson organized the "American Pottery Manufacturing Company," for the purpose of manufacturing various kinds of pottery. By Act of Assembly of January 18th, 1833, the following commissioners were appointed to solicit stock subscriptions: David Henderson, John V. B. Varick, Robert Gilchrist, J. Dickinson Miller, of Jersey City, and Edward Cook,[Pg 95] George Tingle and J. Steele, of New York. During the seven years following there was made at this pottery the first successful competition with England in the manufacture of a buff or cream colored ware of excellent quality, and for the first time in America was adopted the English method of printing transfer in decoration. During the Presidential campaign of 1840 there was made here a large eight-sided water pitcher of cream colored ware; on the four front panels were black under glaze prints of a log cabin above the legend "The Ohio Farmer," and below a portrait bust of W. H. Harrison, with the American Eagle. The mark on the bottom in black under glaze was a flag with the inscription, "American Pottery Manufacturing Company, Jersey City."
In Jennie Young's "Ceramic Art" it is said that at the old Jersey City Pottery the "throwing and turning of earthenware upon the English principle was first performed in America by William and James Taylor." About this time Daniel Greatback, a member of a family of noted English potters, and at one time a modeller for the Ridgeways of Cauldron place, England, came to this factory and designed many ornamental pieces. For its first embossed ware the factory received a medal from the Franklin Institute. One style, a spittoon, was of a glazed white ware with raised white figures on a blue ground, the upper surface fluted and solid blue. About 1850 the name was changed to "The Jersey City Pottery." Many of the best potters in the United States learned their trade here. After several changes, Mr. John Rouse and Mr. Nathaniel Turner became proprietors of the pottery. Mr. Rouse[Pg 96] came from the Derby works, England, and Mr. Turner from the Staffordshire potteries at Tunstall, England. They made porous cups for telegraphic purposes and many ornamental forms in white biscuit and glazed ivory white for decorators. One of the most graceful forms was the Worcester vase, a reproduction of an old pattern at the Worcester works in England. Among others were four different sizes and varieties of Toby jugs, a pitcher with rope and anchor design, a figure of Christ, and Apostle jug; some, if not all, designs of Greatback. On many of the wares portraits were modelled in relief, that of Daniel O'Connell was among the best. The pottery property was sold in 1892 and the old buildings destroyed. It is said that many priceless old moulds were thrown out upon the meadows and broken up. Mr. John O. Rouse still manufactures porous cups within two blocks of the site of the old pottery.
Previous to 1829 there were but few manufacturing interests in Jersey City. In that year several factories were established here, and since 1840 they have steadily increased until they are now so extended and varied, that in a sketch of this limited character they can only be lightly touched upon. While many business firms began here, others have removed to this city from other places; notably the Lorillard Tobacco Factory, which, started in New York in 1760, has grown to be the largest of its kind in the country. It is also a leading company in its care for the three thousand and more of its employees, providing a library, evening schools, sewing classes, and dispensary, besides the most careful sanitary precautions. The Sugar House,[Pg 97] whose output approximates seven thousand barrels a day. The Colgate's Soap and Perfumery Works started in New York in 1806, but have been in Jersey City for many years.
The Dixon Crucible Works, started by Joseph Dixon, the inventor of the Graphite Crucible, first established at Salem, Mass., in 1826, removed to Jersey City about 1850. Mr. Dixon introduced his invention in numerous factories in America and Europe, but the one in Jersey City, with its importations of graphite from Ceylon and Bohemia, its ownership of graphite mines in New England and New York State, and of a great cedar working plant in Florida, is the only factory in the world where all graphite products, crucibles, pencils, stove polish and lubricants are manufactured under the one management.
About 1830, Mr. Isaac Edge established a factory for the manufacture of fireworks, which grew to be the largest in the country, and was widely known in Europe and South America. He was the inventor of the scenic fireworks, so popular to-day, and his manufactory was a training school for American pyrotechnists.
Jersey City can boast a long list of inventors, from Robert Fulton down; Professors Morse and House were residents of Jersey City while evolving the telegraph; and in many of the factories and foundries are numerous inventions of the mechanical experts connected with them; for instance, the weaving and knitting machinery of the fire hose factory are the inventions of Mr. D. L. Stowe, an officer of the company and a resident of Jersey City. The Thompson and Bushnell Foundry Company are inventors of numerous[Pg 98] valuable patents in their line; the list might be extended far beyond our limit. The first Stock Yard and Transit Company in the country was opened at Communipaw in 1866.
I have found the statement that the "first bell made in a mould from blistered bar (cast) steel was made May 27, 1827, at Jersey City." Also that the Kamschatka, "the largest war steamship in the world, in November, 1840, received her machinery at Jersey City." I have been unable to learn to what nation the Kamschatka belonged, nor what foundries furnished her machinery, and made the bell.
In 1829 a Fire Department was started by public subscription; about the same time the Police Department also had its remote beginning in the appointment of seven watchmen. After their term of office expired their places were not filled until, in 1837, four night watchmen were appointed and the City Marshal served by day. In 1844 three men were appointed to serve as watchmen and lamplighters, with a salary of $32 a month. In 1845 they were required to call the hour during the night "until the hour of calling off arrive." Not until 1851 were uniform caps and clubs introduced. In 1859 the first station house was built at Cooper's alley and Gregory street. The present form of police government was started in 1866 and the first mounted police were organized in 1873.
The first attorney to practice law in Jersey City was James Wilson, who opened an office in 1812. The Hudson County Bar dates from the forming of Hudson County in 1840; at that time there were only eight lawyers in this locality. The first court of the new county opened in Lyceum Hall in Grand street, Jersey City, on April 14th, 1840, where it continued to be held until September 19th, 1843, when the court removed to the Newkirk house at the Five Corners, until the new Court House was completed March 11, 1845. The situation of the Court House was warmly debated, each town strongly urging its claims, but finally Hudson City was decided upon, and a site on Newark[Pg 100] avenue was selected for the Court House and Jail; the latter was finished a little later than the Court House, and both were built from trap rock quarried on the site. Until 1843 there had been neither a City Attorney nor a City Physician, but in that year both of these offices were created. In that same year the city introduced street lamps, but at first in only those localities in which the property owners had made application for them. Gas was first used in Jersey City on December 1st, 1852; the streets were first lighted with it a few days later, one hundred and seventy-four street lamps being required. Electric lighting for the streets began about 1884. The first telephone service in the city was in 1878.
In 1834 the New Jersey Railroad and the Paterson and Hudson River Railroad were opened and led to a new era in the history of Jersey City. The New Jersey Railroad extended to Newark, with work in progress toward Philadelphia. Its one car was advertised as "the passenger car 'Washington,' a splendid and beautiful specimen of workmanship, containing three apartments besides seats on top." Regular trips began September 15th, 1834. Eight trips a day were made, going from Jersey City to Newark in one hour and a half. The railroad cut was made by the New Jersey Railroad in 1837, following the line of a water course, and a depression across the ridge, which made it very crooked; the earth from the cut was piled up over one hundred feet high on the land belonging to the railroad back of the Tonnele place. The cars were drawn by horses until the locomotive, the Newark, was used December 2d, 1838.
Beyond where the Boulevard and Pavonia avenue now join, the Railroad Company made a reservoir, which was fed by springs in the hill-side, and from this they supplied their engines with water. Eventually this was incorrectly known as Tonnele's Pond. This road consolidated with the Camden and Amboy in 1867. The consolidation was leased to the Pennsylvania Railroad Company in 1870. After they gained control they straightened the cut by blasting out a roadway through the solid rock. The Paterson and[Pg 102] Hudson River Railroad advertised its "three splendid and commodious cars, each capable of accommodating thirty passengers, and drawn by fleet and gentle horses." In 1848 the road was extended to Sufferns and the Paterson dock was built to accommodate this railroad line. The "Long Dock Company," incorporated in 1856, completed the Bergen Tunnel January 28th, 1861, and in the following May opened the Pavonia Ferry. From 1853 the road was known as the Erie Railroad Company. The Central Railroad of New Jersey terminated at Elizabethport for many years. In 1860 an act was passed authorizing the company to bridge Newark Bay and extend its line to Jersey City. This extension was completed and opened to travel August 1st, 1864. In 1836 the Morris Canal was completed.
Some of the old inhabitants remember when the European Packet ships anchored in the river and their passengers were transferred to small boats to land them. It was in the decade of the 40's that the first trans-Atlantic steamship lines were established, and the Cunard Company, which was one of the earliest, the second I believe, built its docks at the foot of Grand Street, Jersey City, in 1847. Its first steamer, the Hibernia, sailed on New Year's Day, 1848; it was a great gala day for the citizens, and on behalf of the city Mr. Joseph G. Edge fired a salute of 100 guns. Later the White Star S. S. Company had their docks in Jersey City, but eventually both lines removed to New York. At present the Vogemann and American lines have their freight docks here.
In early days the people of Bergen and Communipaw had to go by private conveyance or else walk to the ferry by the Mill road; later stages were run by Peter Merselis from the ferry to Bergen, via Five Corners. There was an office and waiting room at the corner of Bay street and Newark avenue, and in Bergen the stages started from the Columbian Hotel, a building now known as Foye Hall, at Foye Place. After a time omnibuses were introduced, and large open sleighs were used in the winter. Peter Merselis sold out to the Jersey City and Bergen Railroad Company which was incorporated by an act of the Legislature of New Jersey approved March 15, 1859. Under this act they were authorized to lay out and construct a railroad from some point on the Kill von Kull, at or near Bergen Point, to the Newark Turnpike road leading from Jersey City to Newark, with the privilege of constructing one or more branches extending to the several ferries in the County of Hudson, south of Hoboken. During several years they ran a line with dummy engines from the Pennsylvania Railroad ferry to Bergen Point.
The Common Council of Jersey City granted permission to lay a single track of iron rails in Montgomery street, Newark avenue, Grove street to Montgomery street, Gregory street to York street, and Hudson street to Montgomery street. After the railway was laid it was lawful for the company to run cars to be[Pg 104] drawn by horses. These first street cars were peculiar; they were like the body of an omnibus set on a truck; the driver's seat was up on top in front; by means of a strap he opened or pulled shut a door in the rear of the car; the door was reached by two or three steps. Fares were passed up to the driver through a hole back of the driver's seat. At the ends of the route the driver turned the horses and the car turned upon the truck, which was stationary. Long after ordinary street cars were introduced these were used for night traffic, the last car leaving the ferry about midnight.
The Common Council of Bergen granted a franchise in 1864 for the operation of horse cars; this franchise included that part of the city known as Lafayette. As late as 1870 long open sleighs were used in heavy snows during the winter, instead of the cars. For ten or fifteen years the cars were not heated during the cold weather, straw being put on the floor as a protection for cold feet. The first trolley car was run in Jersey City on the Montgomery street line, from Bergen avenue to Monmouth street, in 1890. In 1893 the Consolidated Traction Company took charge, and in November of that year on several of the lines the horse cars were replaced by the trolley system. The extensive car sheds of the Company are on the south side of Montgomery street east of Bergen avenue, and on the north side of Montgomery street between Tuers avenue and Jordan street, partly on the site of Tuers Pond, which was filled in over thirty years ago.
In lower Jersey City the water supply from the wells was inferior and insufficient in quantity. According to Winfield there was quite a business carried on at one time in carting water from the hill and selling it by the pail from door to door. Upon March 1st, 1839, a company was incorporated and authorized to arrange for a water supply for the city, but it failed to accomplish anything. On March 18th, 1851, Edwin A. Stevens, Edward Coles, Dudley S. Gregory, Abraham J. Van Boskerck and John D. Ward were appointed a Board of Water Commissioners to supply Hoboken, Van Vorst and Jersey City with pure water. They employed William S. Whitwell as engineer. Numerous plans were suggested but the commissioners decided upon taking the water from the Passaic at Belleville. Mr. Whitwell began the work near Belleville, August 26th, 1851, and submitted his plan on December 9th of the same year. On March 25th, 1852, legislative authority was given to construct the works. Upon June 30th, 1854, water was let into the pipes from Belleville, and on August 15th, distributed through the city. Up to that date the cost was $652,995.73. At that time the water in the Passaic at Belleville was so pure and clear that the stones could be seen at the bottom of the river. At the same time the board adopted a sewerage plan, a tidal canal from Communipaw Cove to Harsimus Cove, principally along the line of Mill Creek and Hoboken Creek. The scheme pro[Pg 106]vided that it should be open to navigation, and it was believed that factories, lumber, coal, and stone yards would locate along its shores, but it was never carried out. The water and sewerage questions are still unsolved problems of grave importance in Jersey City.
ARMY.
In the Civil War Jersey City was well represented. It is estimated that from the district now included in the city, one man from every five went to the war. From no part of the North was the response to the Nation's need more prompt or more loyal than in Jersey City. The President's call for seventy-five thousand troops was issued on Monday, April 15th, 1861. At the mass meeting held at the Hudson House on Grand street, on Tuesday evening, the first man in the state to sign the rolls of volunteers was James M. Weart, a young lawyer in his twenty-third year. He re-enlisted when his first term expired and served with distinction throughout the war. The Second Regiment of three months men was recruited entirely from this district. At the first call for troops some of the business men of Jersey City advanced the money necessary for their outfits. A camp was formed for the Jersey troops west of the reservoir and was occupied from the beginning to the close of the war. The Second was the only regiment recruited entirely from Jersey City, but different companies joined various Jersey regiments and many men enlisted in New York regiments, but wherever they went they sustained the reputation won in Revolutionary days of the "True Blues of Jersey."
Many of her brave men, officers and privates, were left upon southern battlefields. After the battle of An[Pg 108]tietam eleven families in one block in Fifth street mourned for their dead heroes. Colonel Zabriskie and Colonel Van Houten both fell in battle. Their memories are still cherished and their brave deeds comemmorated in the Grand Army Posts which bear their names. Others were more fortunate and lived to wear the honors won by them. Chief of Police Benjamin Murphy enlisted before he was seventeen, in the 8th N. J. Infantry, which belonged to the famous Second New Jersey Brigade. He was one of less than twenty men of his regiment who served with it continuously from its organization until it was mustered out without having been absent during its service of four years and eleven months. He was promoted from private through the various grades of non-commissioned officers up to captain. After the war he was connected with the post office for a time, and raised Company "C" of the 4th Regiment about 1893. After he joined the police force he resigned from the National Guard. The good order and discipline of the police force is due to his executive ability. He was the author of and secured the passage of "The Tenure of Office" law, which has improved the police force throughout the state. Colonel Robinson of the police force is a war veteran also, but served with a Maryland regiment and came to Jersey City after the war.
Brevet Major General John Ramsey had "few superiors as a stubborn fighter." Several times he received honorable mention in official reports and won his promotions step by step, from 1st Lieutenant up, for "distinguished gallantry." Colonel John J. Toffey entered the Second Regiment a boy of eighteen, re-enlisted in the[Pg 109] 33rd Regiment as Lieutenant, and at Chattanooga was called upon to lead a forlorn hope in the place of two captains who had fallen in the attempt; his "superlatively brave conduct saved the position and enabled the entire line the following morning to press forward and unite the lines of the army of the Cumberland with those of General Sherman's army at the mouth of the Chickamauga." At the moment of success Colonel Toffey received a wound which incapacitated him from future service on the field, but he has continued his military services in the Veteran Corps and in the State Militia. He is the proud possessor of a Medal of Honor, granted by Congress under the Act of 1863, "for distinguished bravery in the battle of Chattanooga, November 23, 1863."
Although Jersey City has been so well represented in the volunteer army, there are but three Jersey City men in the regular army; Captain J. B. Vreeland, now retired, but serving as Quartermaster in the war with Spain, and George B. Arrowsmith and John J. Toffey, Jr., who have been appointed Second Lieutenants during the present summer. The late Major Gaines was in the regular army and served during the Mexican War. He organized a regiment during the Civil War. For a great many years he was connected with the Surveyors' Department of the New York Custom House, and was the delegate appointed by the United States at the Paris International Conference to bring about a uniform system of measuring the tonnage of vessels. He was also prominent in procuring increased cubic space for steerage passengers.
Mr. William Knickerbocker Van Reypen entered the service as Assistant Surgeon December 26th, 1861. Having been promoted through the various grades, he now holds the position of Surgeon General of the Navy. Of good Dutch lineage on both sides of the house, he is proving his sterling inheritances by the masterly manner in which he is meeting the terrible responsibilities of his position in providing for all emergencies in the Medical Department of the Navy in this war with Spain. To Surgeon General Van Reypen the world is indebted for the Hospital Ship in war. At the International Medical Congress, held in Moscow in 1896, he presented the plan which was carried out by the United States Government in fitting out the Solace and Relief during the present summer, which were the first ever used. A most valuable addition to a fleet in war, not only in the relief afforded to the sick and wounded, but in rendering the ships more efficient by leaving them with fighting men only, unhampered by the sick and disabled. There is so little space on board men-of-war which can be utilized for hospital purposes that the chances of recovery for the wounded are largely increased. Civilian doctors who have visited the Solace are enthusiastic over the perfection of its arrangements for the sick and wounded. It is a marvel that a ship not built for the purpose could be so well adapted to hospital needs. Jersey City may well be proud of Surgeon General Van Reypen.
The only other representatives of Jersey City in the navy during the war, so far as I can learn, were in the[Pg 111] volunteer navy: Acting Master James M. Van Boskerck, who was in command of a guard boat at Alexandria, Virginia; Dr. Forman, who served as assistant surgeon during the war, and Mr. Daniel Toffey, who acted as captain's clerk for his uncle, Captain John L. Worden, on the first Monitor that was built and went into service as an experiment in 1862. Mr. Toffey acted as aid in carrying orders during the famous battle between the Monitor and the Merrimac. Of the nine monitors ordered by the government during the Civil War, six were built in Jersey City shipyards. Aside from the above named, I have been unable to learn of many other citizens of Jersey City who have served in the navy. About 1835, Commodore Wetmore built a large white house on Newark avenue below Baldwin avenue where he and his family lived for many years. At one time he was in command of the Constitution at the Brooklyn Navy Yard. At the building of the Hudson County Court House, Commodore Wetmore determined the astronomical position and the following is the latitude and longitude of the observation spot:
Latitude 40°, 43“, 50", north.
Longitude 14h., 48m., 44., 1s., or 74°, 3“, 40.5", west.
At present Lieutenant Harry Phelps, who graduated from the U. S. Naval Academy in the Class of 1880, Lieutenant Charles Phillips Eaton of the Class of 1883, and Lieutenant Philip Andrews of the Class of 1886, are, I believe, the only line officers in the navy from Jersey City.
The Journal's History of Jersey City gives an interesting sketch of the origin and development of the[Pg 112] National Guard of the state and ascribes to Mr. William E. Rogers, a former resident of Hudson City, the honor of being the founder of the 4th Regiment and of the National Guard of New Jersey. He was a member of the National Zouaves, a New York company, drilled by W. W. McChesney, the former drill master of the Ellsworth Zouaves. This company was one of the first to enlist for two years in the beginning of the Civil War. During the first year Private Rogers was severely wounded while on picket duty and incapacitated for active field duty, but he obtained a detail as chief clerk of the General Hospital, now the Soldiers' Home at Fortress Monroe, where he served until mustered out of service. After his return he became the teacher of a Bible class of forty boys in Simpson M. E. Church on Central avenue. The boys induced him to give them instruction in the manual of arms. A company was formed which was known officially as "Company A, unattached, N. J. Rifle Corps." Its first public appearance was in a parade at Newark, on Washington's birthday, 1865. It turned out eighty strong, in a blinding snow storm, and by its discipline and soldierly bearing won the commendation and friendship of Governor Ward and Major General Runyon, the reviewing officers.
There was much opposition to Company A by the officers of the old Hudson Brigade, of which there was not left a single uniformed and equipped company. Through the efforts of Mr. Rogers a committee was appointed to draw up a law to conform with the National Guard Act passed by Congress. General Runyon, Colonel Plume and Colonel Rogers were the[Pg 113] committee. After much opposition the Legislature passed the law and Governor Randolph signed the act March 9th, 1869. Other companies were formed: Company B, by Captain Bullard; Company C, by Captains McLaughlin and Murphy; Company D, by Lieutenant J. J. Toffey; Company E, by Captain Henry G. Shaw; Company F, by Captain John B. Randolph. General orders were issued creating the six companies into the 4th Regiment, N. J. Rifle Corps, with Colonel William E. Rogers, Lieutenant Colonel C. G. Van Reyper, Major William B. Shafer. By a general order issued by Adjutant General W. S. Stryker on April 14th, 1869, these six companies and Company G of the Second Regiment, N. J. State Militia, were assigned to the Fourth Regiment, First Brigade.
Colonel Rogers was appointed Inspector General on the Staff of General Runyon, and for more than a year was constantly occupied in securing compliance throughout the state with the National Guard Act. The regiment gave an inaugural concert and hop at Kepler's Hall (now the Academy of Music) on the evening of May 12th, 1869—"one of the most brilliant events in the history of the city up to that time." For twenty-five years their armory was at 25 and 27 Newark avenue. The new armory in Bergen avenue was completed in February, 1895. The regiment has served honorably on several occasions in suppressing riots, both at home and in other states; it has joined in numerous parades, and has acted as Guard of Honor at the funerals of several notables. At the State Camp its members have nearly all qualified as marksmen at[Pg 114] the state rifle ranges. One of its early officers, Lieutenant Colonel Shaw, was the author of the competitive system of rifle shooting as practiced in the United States. He was instrumental in starting the Creedmoor Range, which was known for years as the American Wimbledon, but has since been surpassed by the New Jersey State Range in the variety of ranges for different shooting.
NAVAL MILITIA.
The Naval Militia of New Jersey was organized in the spring of 1895. The members are largely from Jersey City, Newark and Hoboken. The Navy Department allowed them the old man-of-war, the Portsmouth, which had been dismantled and consigned to "Rotten Row." The Jersey sailors have fitted her up with masts and rigging and again she is fit to go to sea and has become once more a school to turn out thorough going seaman. In addition to the yearly cruise on the Portsmouth, the militia have drills, inspections, etc., on board other men-of-war. In 1897 these drills were aboard the Maine off Tompkinsville, and from the official report of the Board of Naval officers to inspect them, the following data is taken:
"The Battalion of the East:
"Fifteen commissioned officers; eight chief petty officers; one hundred and eighty-six officers and enlisted men.
"The commander, executive officer and navigator are elected by majority vote of all the commissioned officers; the adjutant, ordinance officer, paymaster, surgeon and assistant surgeon are appointed by the [Pg 115]commander; the divisional officers are elected by the men of their divisions. Three of the commissioned officers are graduates of the Naval Academy. Another passed two years and seven months at the Naval Academy; and two are from the merchant service.
"The state appropriations average about $7,500 and the balance of the fund needed has been contributed by the citizens and by the members of the battalion.
"The armament consists of:
"Main battery; eleven 8 inch Dahlgreen M. L. smooth bore; one converted Parrott B. L. R. Secondary battery; one 1 pounder Hotchkiss Repeating Rifle, mark II; two 3 inch B. L. R. (Navy Howitzer 350 pounds); one Gatling, long. Of the guns, all the secondary have field carriages. Boat mounts are to come out of the U. S. appropriations. Small arms: 200 Lee rifles, 2d model; 45 calibre and accoutrements; 150 Navy revolvers; 150 cutlasses; 150 belts, boxes and frogs.
"The boats include 1 steam cutter, 3 cutters, 2 whale-boats, 1 gig, and 2 dinghy. The signal outfit consists of the International Code, Navy numerals and wigwag flags.
"The uniforms of the officers are similar to those worn in the regular Navy and that of the petty officers and men of the Navy pattern.
"Tents are furnished when required by the Quartermaster of the state. The battalion owns a complete outfit of mess gear.
"Drills and exercises on board ship: Seamanship, compass, log line, boats, signals, ship routine and discipline. Onshore: Infantry, artillery, signalling.
"The men of the Engineers' division have technical instruction at Stevens' Institute, on steamers of regular lines running out from New York, and in operating and caring for the steam plant on board of the Portsmouth."
On several occasions the Battalion of the East has won praise and distinction in public parades, and during the present year have acquitted themselves with honor in the war with Spain. Among the first volunteers to be called into service last spring five of their men had charge of a signal station at Barnegat. Detailed to the Badger they took part in blockading duty off Cuba, where for several days the Badger was the flag ship. The Badger is the only ship manned by Naval Militia that captured any prize, and the Jersey boys are very proud of their record, having captured three.

U. S. S. Portsmouth.
The plot an Washington street and South Cove, originally designed for a market site, was used on several occasions for cholera and small pox patients. In 1868 the city decided to use it for the City Charity Hospital. In 1882 the city erected a larger hospital on Baldwin avenue near Montgomery street. In 1885 the name was changed from Charity to City Hospital. At present there are two hospitals, the Warden's house, the stable and dead house. It is under the police management. The surgeons and physicians gave their services: George O. Osborne has been Warden since 1882. Samuel D. Key, the pharmacist, has served since 1870, and much of the excellence of the hospital is due to the efficiency of these two men. Christ Hospital, an Episcopalian institution, was first started in the old Tonnele mansion on Magnolia avenue. After a few years Dr. Abercrombie rented the building, and largely through his efforts the hospital was made a success. In 1889 the new hospital was opened on Palisade avenue, and this year a large addition is being made to the building. In 1890 a training school for nurses was organized, which has graduated highly skilled and efficient nurses. There is an out-door department which gives medical aid to a large number. The maintenance of the hospital is managed by the council, assisted by the hospital guilds.
St. Francis Hospital was founded in 1864, by the "Sisters of the Poor of St. Francis," in a small way in[Pg 118] a private dwelling on the northeast corner of old Fourth and Coles streets. Now they have the most complete hospital in the state, due, says the Journal's History of Jersey City, wholly to the tireless work and activity of the noble order of sisterhood who have charge of it. It is not endowed, is distinctly a charitable institution, receiving neither state nor municipal aid. Its charities are free to all, irrespective of creed, color or nationality. Its a splendid evidence of the devotion to duty, indomitable courage, perseverance, energy and self-denial of the Sisters. The number of patients treated annually at St. Francis exceeds that of all other hospitals in Jersey City.
The Home of the Homeless, started by a few ladies in 1883, now situated at 266 Grove street, has accomplished a vast amount of good in sheltering hundreds of children and a few homeless women. The Children's Friend Society was incorporated in 1864. They established the first Children's Home on southeast corner of Erie street and Pavonia avenue, but in 1874 built the present home in Glenwood avenue, near West side avenue. Here destitute homeless children are cared for, clothed and educated, trained to become self supporting men and women. One of the most worthy charities of the city. The Home for Aged Women grew out of the efforts of a few ladies who started a fund in January, 1866. In 1868 the Society was incorporated. For seventeen years the Home was at 131 Wayne street. In 1885 Mrs. Moore, a Scotch lady, gave the Society her property on the corner of Bergen and Fairview avenues, in consideration of a home in the institution for the remainder of her[Pg 119] life. They have added to the building, and it is now a comfortable home for a large number of old ladies. The Catholic Societies support the St. Michael's, St. Joseph and St. Mary's Orphan Asylums, each with a school connected.
One of the most beneficent institutions of Jersey City is the Social Settlement, the Whittier House, founded by Miss Cornelia Bradford, in the old Clark house, 179 Grand street, in May, 1894. Miss Bradford is the head worker, and is assisted by five "resident workers" and fifty "out workers," who come in from neighboring towns and Jersey City, to take charge of certain departments. The members of the various clubs and classes pay small fees which are merely nominal. The work has been extended to such a degree that last year it became necessary to hire another building and still another will be required this year. The work includes a kindergarten, medical and dental dispensaries, a sewing school, classes in dancing, physical culture, in household service (the kitchen garden) and cooking; numerous clubs, among which are the "Mothers," the "Newsboys," "Working-Girls," the Civic League, etc.; a Penny Provident Fund, a station of the Public Library, and altogether too many branches of usefulness to be enumerated here. In another part of the city Mrs. Brice Collard has a flourishing sewing school of over six hundred members; also a Mother's Club, both of which do much good work.
There are in Jersey City over fifty clubs of various kinds. A few own handsome club houses, others meeting in hired rooms or at the homes of the members. So far as I can learn the Everett was the pioneer club of the city, and therefore justly gives precedence to the literary clubs. In 1865 the "Everett Literary Union" was organized, and met in a room over a store on Newark avenue. Debates and essays on various topics were the order of proceedings. Judge Dixon started it, and he, Judge Collins, Mr. William Brown and Mr. Walker were among the twenty-five gentlemen who composed the society; most of whom now belong to the Cosmos Club. The Cosmos Club was founded some years ago by the Rev. Dr. Stoddard, with the original intention of a "Membership from different professions and employments, that each might speak with authority upon the particular branch of work in life to which they were devoted." For many years they met at houses of the members, but of late years their method is to meet once a month at the Washington Hotel, dine, and, after dinner, have a special speaker upon some stated subject, followed by a general discussion. Washington's birthday is their High Festival occasion. A few years ago they made an innovation upon their former custom by inviting ladies to their annual festival. In February, 1897, the Odd Volumes were their guests—a red letter occasion in Jersey City club life. In April, 1898, the Odd Vol[Pg 121]umes enjoyed the pleasure of entertaining the Cosmos Club, at an "Authors' Reading" by Mrs. Ruth McEnnery Stewart.
The Ęsthetic Society, a literary club of ladies and gentlemen, was founded by Mrs. Erminnie A. Smith. In the records of Jersey City no name stands higher than that of Mrs. Smith, whose home was at 203 Pacific avenue. She was a woman of wonderful magnetic and personal influence, of rare culture, great ability and scientific attainments, a profound student along many lines, an expert in geology and mineralogy, an authority upon "Indianology." Her talents were widely recognized. In the interest of the Ethnological Bureau she made personal investigations into the history, legends and folk-lore of the Iroquois Indians, and prepared a dictionary of the Tuscarora language. She was an honorary member of the British Archeological Society, a member of the American Archeological Society; the first woman elected a member of the New York Academy of Sciences; not only a member of the American Society for the Advancement of Science, but also Secretary of the Section of Anthropology. Withal she was a most womanly woman. Jersey City owes to this gifted woman a debt of gratitude, not alone for her influence in awakening a love for science and literature among the young people, but for forming the Ęsthetic Society, and in bringing hither the most celebrated people of the day, both American and foreign visitors, to our shores. She developed an interest among Jersey City women in intellectual pursuits which has grown and deepened with the years. May her memory ever be held in loving remembrance. The[Pg 122] Ęsthetic Society was composed of women and men, many of whom were prominent in literary circles. The younger members of the society studied history and literature, and, aside from the lectures from celebrities, interesting essays were prepared by the members. At the death of Mrs. Smith, in 1886, the society ceased to exist. A short time after a few of Mrs. Smith's friends, principally ladies of Jersey City, raised a sum of money to create a prize and presented it to Vassar College, the interest of which is to be given in two prizes each year for the best work in geology and mineralogy. A fine portrait of Mrs. Smith was also presented to Vassar. This was considered a most fitting memorial to one who was always helpful to others.
In the fall of 1887 Miss Cecelia Gaines proposed to a few friends the formation of a club for the study of Literature, and the Odd Volumes came into existence with a membership of eight which was soon increased to the limit of twenty-five. After a few years the limit was increased to thirty-five. The meetings are held at members houses. That it has become an ideal woman's club is proved by its long list of waiting candidates for admission, and the desire for invitations to its regular meetings and its special festivities. While the club has accomplished much good and serious work in its literary and historical studies, it has not lost sight of the social feature which has been such an important factor in its success and popularity. Miss Gaines is the president. In that office the club will not allow any change, but with the other club officers rotation in office is the rule.
In 1894 was formed the Jersey City Woman's Club, which has a membership of over two hundred and is unlimited. It is a department club, its several sections being Education, Woman's Exchange, Philanthropy, Town Improvement, Home, Literature, Music and Art. "Its object shall be to awaken interest in subjects which especially concern women; to stimulate inquiry in questions of public significance, and to promote effort toward social and educational advancement. Motto: 'In great things, unity; in small things, liberty; in all things, charity.'" Miss Gaines was the first president; she was succeeded by Mrs. Alice May Scudder. The meetings are held at Hasbrouck Institute, the first Thursday in each month.
The Ramblers is a young ladies' literary club, connected with Hasbrouck Institute. The Open Hand is a club in the northern part of the city, for the study of history and literature; although still young it has made most notable progress. The Ceramic club is a society of ladies who are enthusiastic students of china decorative art, and of the history of pottery and its associated literature. At their social meetings there is a fine display of artistic work of the members. Once a month they usually have a talk by a specialist upon some branch of their work. The women's clubs of Jersey City are all represented in the New Jersey State Federation of Women's Clubs, which was organized in 1864, in response to a call of the Woman's Club of Orange, at Orange, with Mrs. Yardley, of Orange, as its first president. In October, 1896, its convention was held at Jersey City in the Bergen Reformed Church;[Pg 124] a very notable occasion. At that time Miss Cecelia Gaines was elected president. During the past summer she ably represented the state at the convention in Denver, Colorado.
The Orion Rowing Association, the pioneer boat club of Jersey City, was organized in August, 1872, and Judge J. H. Lippincott was its first president. The first club rooms were on the southwest corner of Newark and Baldwin avenues, those formerly occupied by the Hudson City Free Library. The first boat house was a fat factory on the meadows, a quarter of a mile from the Hackensack River, but the enthusiasm of the members was so great that they carried their four-oared barge to and from the river until they were able to secure better quarters. Through Mr. Levering's efforts Gill Ward, one of the famous Ward brothers, at one time champion oarsmen of the world, coached the Orions in the fall of 1872, and again for several weeks in the following year. In October, 1876, the Orions united with the Hudson Athletic Club, which had been organized by Messrs. H. and C. Hoe, C. Rooney, F. Hill and W. H. Kuran, and was henceforth known as the Orion Rowing and Athletic Association. They then made their headquarters in the Beach block, opposite the Court House, where they fitted up a fine gymnasium, with an instructor from New York. These gymnasium privileges were extended to a junior class.
For many years their receptions were social events and largely attended by prominent people. Exhibi[Pg 125]tions were held every spring and autumn for many years at the West Side Driving Park. The inaugural exhibition, on Decoration Day, 1877, was a red letter day in athletic circles. There was the largest list of athletic games on record up to that date, with entries from most of the prominent amateur athletes in all lines, from all over the United States. Stages were run from the ferries and the elevator to the West Side Driving Park. From that date the Orions gained and held a most desirable reputation for honor, fairness and excellence in athletics, and became a very popular club. Referees and judges, on field days, from the Orion members were selected by athletic clubs, not only in New Jersey, but in other states. There are treasured in the club annals a long list of names of athletes who won on numerous fields honor and medals. In this same year, 1877, the club built their boat-house on the Hackensack River, at the foot of St. Paul's avenue, twenty by one hundred and twenty-five feet. On the lower floor the association boats are kept, eleven in number—a barge, two four-oared gigs, two pair-oared gigs, three single gigs, and one four-oared shell. The second floor is used for lockers and dressing rooms, with tables and chairs. A two-storied veranda extends across the building, and the upper one makes a delightful lounging place for the club members. From the flagstaff floats the blue and orange flag of the Orions. The boat-house occupies an exceptionally fine location. It fronts upon deep water, with a straightaway course of a mile and a half, where a dozen boats could be sent off abreast. At no time are they prevented from rowing by rough waters or heavy winds.[Pg 126] Every year the Orions hold a regatta, but no entries are allowed from other clubs. Competition and honors are strictly among themselves. There is a long list of efficient oarsmen whose names are honored in the club. Orions are famous for their jolly good times; with all of their hard work, they have kept up the social side of club life, and are deservedly popular. The Hudson Boat Club, which was organized about the same time as the Orions, had its headquarters at Communipaw Cove, near the Sugar House, and was at one time a very popular club. The Jersey City Athletic Club has a boat-house, and rowing forms a part of the athletic exercises.
In July, 1877, were organized two Gun Clubs in Jersey City—the Jersey City Heights and the New Jersey—both of which were in existence for several years and achieved some very fine records in pigeon and ball shooting. The Jersey City Heights Gun Club was organized July 11th, with the object of "the education and advancement of its members in the art of wing and trap shooting; also for the enforcement of the game laws of this state." The rules required that the butt of the gun should be clear below the elbow when the shooter called "pull." The club rooms for many years were at the northwest corner of Oakland and Newark avenues, and their grounds were at Marion, where there were held many interesting shooting matches among themselves, and with other clubs. Under their auspices were held exhibitions by such celebrated shooters as Dr. Carver and Capt. A. H.[Pg 127] Bogardus; and numerous tournaments open only to amateurs, besides the regular club days, when the members contested for their club prizes, the fifteen and twenty ball badges or the cup.
One of their most celebrated contests was with the Fountain Club, May 31, 1883, at their grounds, at Prospect Park Fair Grounds, L. I. The Fountains were one of the most celebrated clubs in the United States, having won the Richmond Diamond Badge in 1882, at the New York State shoot; also the Dean Richmond cup valued at $1,000. The score was twenty men, ten birds to each man, twenty-five yards rise, both barrels, a friendly match for the birds only; the judge for the Fountains, the referee and trap puller were all Fountain club men, while a member of the New Jersey club was judge for the Jersey City Heights Gun Club. Mr. Alfred Heritage was captain of the Jersey City Heights team. The score was:
| THE FOUNTAINS | THE JERSEY CITY HEIGHTS | ||||||
| 1st | squad | 43 | 1st | squad | 43 | ||
| 2d | " | 37 | 2d | " | 43 | ||
| 3d | " | 36 | 3d | " | 43 | ||
| 4th | " | 45 | 4th | " | 46 | ||
| —— | —— | ||||||
| Total | 161 | Total | 175 | ||||
The story is still told among the old members of the club who claim that under the circumstances and rules of carrying the gun the record has never been beaten.
The New Jersey Gun Club was organized July 18th, 1877. Its object to protect and enforce the Game Laws of New Jersey; to foster and encourage the improvement of the dog and gun; to promote friendly intercourse and generous emulation among sportsmen,[Pg 128] and also to engage in such sports, games, and matches as desired by the members. The shooter was required to hold the butt of the gun at the hip until the bird was on the wing. The rifle rules were the same as those adopted by the State National Rifle Association, with the exception of the arms, which were decided by a two-third vote of the club. Mr. Thomas W. Harrison was a prominent member, also Mr. William Hughes, who was also a member of the Jersey City Heights Gun Club, and known as "Old Reliable," for his uniformly good scores. The medal of the New Jersey club was a retriever's head holding in its mouth a woodcock with diamond eyes, costing $80. The club prize was a beautiful silver cup costing $200. When the club disbanded, about 1885, the members competed for final ownership of these and Mr. John Pearson won the medal, and Mr. Hughes the cup.
The New Jersey, Palma (which began as a Rifle Club), the Jersey City Athletic, the Cartaret and Catholic Clubs are social clubs and immensely popular. The most of them extend many privileges and courtesies to their women friends. The Catholic Club was organized by Father Kelly, now of St. Mary's Church, Hoboken, in 1892, and was an outcome of his desire to provide a place of recreation for the young men and women of his church. It was the first club in the city where young women had free access and right as associate members to the use of the reading room, library and bowling alley. I believe that they are still restricted to certain days in that respect, and in voting they are[Pg 129] not upon a perfect equality with the masculine members, but what they have is a long step in the right direction, and has been a very great success. The club now has a membership of one thousand, and the plan is being followed by the clubs of the other Catholic churches.
The most prominent are the Union League and Hudson County Democratic Society, both of which own handsome club houses on York street facing Van Vorst square.
About 1866 a few gentlemen in Bergen formed the Bergen Library Association. They collected subscriptions and organized a library of one thousand volumes. A room was given for their use in Library Hall and Major Gaines acted as librarian and secretary. After a few years the interest in it died out and the books were sold. In 1867 a few gentlemen in Hudson City formed a Free Library Association and hired a room on the southwest corner of Newark and Baldwin avenues for the library. Books were given and bought until quite a respectable beginning was made. The ladies formed an aid society to help raise funds to start and support it. It existed for a few years, and then, for lack of funds and public interest, was discontinued. The books were packed and stored in a stable belonging to one of the trustees. In 1873 the Board of Education was authorized to establish a free library, with an allowance of $1,000 per year. It was kept at the High School and was open on Saturdays only. It was patronized principally by the pupils and teachers of the High School; in fact, there was a general impression abroad that none others were entitled to the privilege of the library.
In 1884 the New Jersey Legislature passed a law providing for free libraries in cities where the provisions of the law were accepted by the people at the general election. At the first election held, through indifference of the voters, there was not a majority in[Pg 131] favor of a library, and the matter rested until another opportunity was given in 1889. At the April election of that year the requisite majority was secured. In May the Mayor appointed a Board of Trustees to create a library. They were Dr. L. J. Gordon, Michael Murray, W. C. Heppenheimer, Nelson J. H. Edge and Charles S. Haskell. The Mayor and City Superintendent of Schools, ex-officio members. The library was opened July 6th, 1891. Mr. George Watson Cole was the first librarian, but was soon succeeded by the assistant librarian, Miss Esther E. Burdick. In the beginning the library met with many obstacles from the politicians, but owing to the indefatigable energy of Dr. Gordon and some of his colleagues, these and all other hindrances were overcome. A sinking fund was started for the purchase of lots and the erection of suitable buildings. The site purchased fronts on Jersey avenue, with fifty-one feet on Montgomery street, and fifty feet on Mercer on the block east of Jersey avenue.
The library has established fifteen stations. These will be increased as there is demand. In the reading room three hundred and ten periodicals and newspapers are on file, and it is well patronized every day of the year. The reference room is a greatly appreciated feature of the library, and is patronized by men, women and school children, who always find in Miss Burdick a courteous, kindly, interested assistant, one who always seems to know just where the needed knowledge is to be found. The very superior cataloguing of the library is due to Miss Burdick. While she is invaluable to all who frequent the library, her warm[Pg 132]est sympathies seem to go out to the school children; to help solve their difficulties is her greatest delight. The cherished hope of her heart is that in the new library building there may be a children's room, well supplied with the very best juvenile literature. She recognizes fully the importance to the future of our city of the proper direction of the minds of the children, and in this line is doing most noble work for her adopted city. The library has many excellent features, notably the system of book circulation among the schools—the works in German, French and Italian—and its department of books for the blind. Jersey City may well be proud of its library and of its trustees and officials.
Jersey City is lamentably deficient in parks. Before the city was first established, some say that there was a small park in front of Lyons Hotel, others assert that there was only one willow tree there. After the city came into existence there was for many years, on the site now occupied by the brick-yard, south of Essex street, between Essex and the Canal, a pleasure resort called the Thatched Cottage Gardens, with trees, flowers and vines, where there was music, balloon ascensions and games, and ice cream served in the summer houses and arbors. A place very popular, not only with Jersey City people, but also with many New Yorkers. It was the scene of many interesting events, among others it is said that Jenny Lind sang there. An interesting illustration of the growth of local expressions had its origin in a little incident connected with a visit of Bergen boys to the Thatched Cottage Gardens to see a celebrated aeronaut of the day, named Gilley. After their return home the boys arranged a balloon ascension of their own in the barn belonging to the father of the chief actor, who by means of ropes fastened about him and thrown over the beams above, holding an open umbrella, was drawn up by the other boys to what he considered a proper height, then bidding them let go, he expected to sail off by means of his umbrella, but instead, came suddenly to the barn floor, with a broken leg as the result, amid the derisive jeers of his mates, "You're a Gilley!" To this day[Pg 134] the term is used among Bergen children when an over smart scheme of a mate proves a failure.
In Bergen the old orchard on the Merselis farm, near Orchard street, called the Merselis Grove, was for years a resort for picnic parties. To-day there is the Caledonia Park; the Blakely Wilson Homestead, on Baldwin avenue, belonging to a private corporation and hired out to associations for picnic and games. The only city parks are Van Vorst Square and Hamilton Park, which were originally given to the town of Van Vorst, the first by the Van Vorst family and the other by John B. Coles, the founder of the town, and the four park corners at the intersection of Washington and Grand streets. A few years ago, when there were still acres of woodland between Jersey City and Bergen Point, where people could go for a day's outing, there seemed less need for city parks, but with the growth of the city and the vast increase of the manufacturing population, there is necessity for the establishment at different points of small parks and play grounds as breathing places for the crowded portions of the city. At present the Boulevard or County road is the great resort on Sundays and holidays, when it is crowded with people in vehicles of all characters, on bicycles and afoot.
What of Jersey City to-day? It has been said that when the plan of the tide-water canal on the western border of the little city started on Paulus Hook failed to be carried out, that it was a blow to the prosperity of the city. Perhaps it was, but when the consolidation of all the towns in Hudson County was started in 1869, the movement embodied greater possibilities for the city than were ever dreamed of by the associates. The first effort failed of its complete realization, but it will eventually be carried out. Last winter legislative action was begun looking to the including of the whole of Hudson County in the Jersey City of the future, thus giving it an area of nearly thirty-nine thousand acres, and a magnificent water front of about seventy miles along the Hudson, the Kill von Kull, Newark Bay, the Passaic and the Hackensack, giving the city almost unlimited business possibilities. The city is already the center of several of our great railroad lines, and year by year is steadily growing in commercial strength and population, which is now nearly one hundred and ninety-six thousand. Situated as it is, it combines magnificent residence locations along the Heights, from the northern limit of the county to Bergen Point, with the business sites of the lower portions of the city on either side of the dividing ridge. Nature has been lavish of her gifts to our city; from almost any point of the Boulevard are magnificent views, unsurpassed in[Pg 136] any city in the country. We already have many beautiful streets and buildings, both public and private residences, and each year is adding to their number.
An interesting feature of the city, and one that is a matter for congratulation, adding, as it does, to the historic interest of the town, and is a connecting link between the city of to-day and the early settlers who founded here the first village in New Jersey, is the fact that there are still in the limits of Jersey City quite a number of old houses built upon the Dutch plan, although there are but few dating beyond the present century. The Gautier house, on New York Bay, for some years the home of the Greenville Yacht Club, was built in 1760 by Captain Brown, and called "Retirement Hall." In the old days it was the scene of a lavish hospitality, and gay hunting parties were often gathered there. Captain Brown was the owner of slave ships, and the slaves were kept in the large cellar of his house, where the rings and staples to which they were chained were still in the walls, and, with the large fire-place, remained until a few years ago. The house became known as the Gautier house through the marriage of his daughter and heiress with Mr. Gautier. It has been held by several different owners, the latest of whom, the Lehigh Valley Railroad Company, are about to remove it. People who have resided there tell interesting stories of hearing the "swish" of oars and grating of boats upon the beach, followed by the tramp of feet from the shore to the cellar, and groans, with the rattling of chains. Originally the house had a double veranda across the front, and within the memory of the present generation it was still a beauti[Pg 137]ful place, with fruit trees and grape-vines planted by the original owner, still in existence not many years ago. Mr. Brown was a devoted patriot, and served the country in many capacities. Then there is the old Midmar house, between Gates avenue and the Morris Canal, probably built by a Vreeland, some time in the last century. The Daniel Van Reypen house, at 320 Fairmount avenue, was also built before the Revolution; a story and a half Dutch house, originally with two wings. When the street was laid out one wing was cut off, leaving it with the gable end to the street; otherwise the house has not been changed much, only as time has brought ruin and dilapidation.
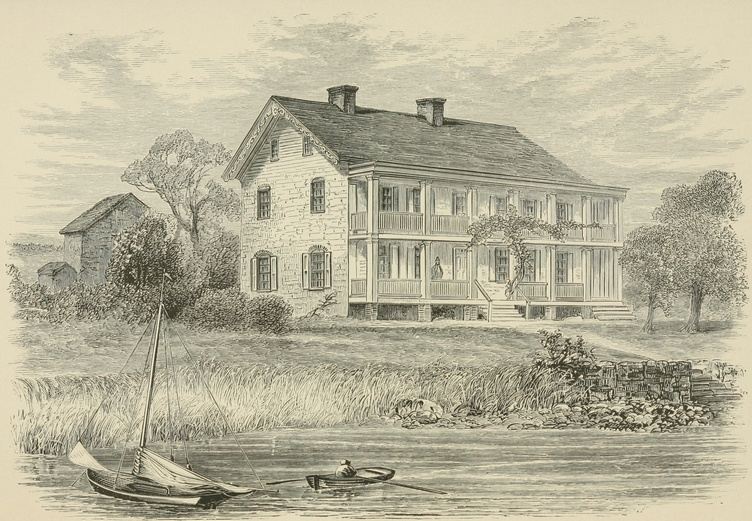

Retirement Hall.
Old Sip Mansion.
Interior of Old Sip Mansion.
The other old houses that are left date from the early part of the present century. The Van Reypen house, 201 Academy street, a little west of the site of the original house built in 1660-61, was built in 1802. The Sip house on the corner of Bergen avenue and Newkirk street, which, like the Van Reypen house has sheltered four generations, is probably about the same age. The Van Horn house near Philip street, fronting the New York Bay, was built in 1804, on the site of an earlier house. It was here that Washington Irving wrote his "Knickerbocker History of New York," and it is to this house he refers in his sketch of "the House of the Four Chimneys." It has been remodelled, but the lower portion remains not greatly changed. 631 Bergen avenue was built in 1805, a square two-story brick and stone house, with an extension at one side. The old tree which formerly stood in front of this house, about which were clustered many stories connected with Washington, was an English elm and[Pg 138] probably set out about the time that the house was built.
Then there are the Newkirk houses, built by the two families of that name. The one on Newkirk street and Tuers avenue, a little northeast of the site of the original house, was built in 1810. In the parlor is the high, carved wooden mantle, and the wide hall has the Dutch half doors, although the upper and lower portions are now nailed together. It is said that the father of the present owner, Mr. Gerritt Newkirk, who died in 1893, shot in Greenville, in 1873, the last wild deer seen in Hudson County. The house 52 Sip avenue was built by Mr. John Newkirk, on part of the Newkirk farm. The stone house at 36 Church street was built in 1829, by a member of this family, Mr. Henry Newkirk. The other Newkirk family built the old house on the east side of Bergen avenue, between Magnolia avenue and the bridge, also the house on the southwest corner of Bergen and Jewett avenues, which has been remodelled and is now one of the prettiest houses in Bergen.
Another very interesting old house which has been remodelled is the Halmagh Van Houten house, west of the reservoir, on Summit avenue near Germania street. On the southeast corner of Bergen Square stands the DeMott house, still in most excellent condition. The old house on the southwest corner of Glenwood and Bergen avenues, was built about seventy-five years ago by Mr. George Tise, upon the site of the old Stuyvesant tavern, largely of the material of the former building; in the rear wall is the date stone of the old house, marked "P. S. 1762." This house was a tavern within[Pg 139] the memory of comparatively young people and was quite celebrated for the good dinners and suppers served there. Fricasseed snapping turtle and roast pig were among the choice dishes. The barns and sheds were on what is now the opposite corner of Glenwood avenue, and here, the people who came from a distance, put up their teams during the Sunday services.
At the Five Corners are several interesting old houses; Riker's Tavern on the southwest corner of Newark and Summit avenues, and Coulter's general store, now a grocery store and dwelling house, on the southeast corner of Newark and Summit avenues. Coulter's Tavern was on the site now occupied by the Avenue House; the old stone house built for a tavern by Mr. John Tise, on the northwest corner of Newark and Summit avenues, and the old building, formerly a store kept by Nicholas and Justus Jerolaman, on the northeast corner of Summit and Hoboken avenues. It is said that at the Corners, just in front of the point where stands the Avenue House, there was formerly a Liberty pole, probably erected about 1812-14, but at a St. Patrick's celebration, not long before the Civil War, there was found in the early morning a St. Patrick hung in effigy upon it; the indignant Irishmen cut the pole down and it was never replaced.
Many of these old houses are a story and a half, some fronting the street, others with the gable end to the street, with dormer windows in the sloping roof which extended out over the porch, sometimes upon both sides of the house; in others the porch was only in front, and in the rear the roof sloped to within a few[Pg 140] feet of the ground. One peculiarity in many of these early houses is that instead of using lathes, the "brown coat" of plaster was mixed with straw and thickly plastered on to the stone. Almost invariably an extension was built at one end, with the roof a few feet lower than the main part. In later days this was the kitchen, but in olden times the kitchen was a detached building, and the slaves slept in the loft. In the main part there was a wide hall, usually through the center of the house, but sometimes at one end, with the Dutch half doors at either end. During the summer months the family meals were usually served in the hall; they used a "comfore," a sort of chaffing dish with hot coals, upon which the kettle was set to boil the water for the tea. During the winter the living room was also the dining room. There are still preserved in some of these old houses, choice heirlooms of quaint furniture, rare old Delft, Prints, Psalm books with great silver clasps, a few old Dutch Bibles with board covers, and interesting relics of many kinds, of which an occasional glimpse is given at some loan exhibition, but usually they are carefully guarded from profane eyes.
In 1806 the United States Government became possessed of the property on Palisade avenue between Hoboken and Newark avenues. Here was situated the old building known as the Arsenal, which served as arsenal, barracks, and hospital during the war of 1812-14, and once again as barracks in the war of 1861-65, the Anderson Zouaves and the New York troops being quartered there. Several of the soldiers who died there in 1812-14, are buried in the west corner of the cemetery on the southwest corner of Vroom street[Pg 141] and Bergen avenue. After 1865 the old Arsenal was used as a tenement house until it was torn down, about twenty years ago. Although all trace of it is now lost, the memory of it should be preserved.
Two very interesting houses in lower Jersey City are on Wayne street, of Ionic architecture, built about seventy years ago—one, No. 95, by Cornelius Van Vorst, and the other by Dr. Barrowe—and so carefully and well built that to this day they have needed no repairs. The houses are forty-seven feet front by fifty five feet deep. The columns in front are twenty-eight feet high. The doors are of solid mahogany, and it is said that the original window glass was tinted and imported from Venice. The veined marble mantels were also imported. In the wide central hall was a great stove, with pipe running up through the hall above. This, with the grates in each room, was the only means of heating the house. When built the houses were the only ones on the block, but that was too limited a space for houses as large as those.
Another very interesting old place was the Tonnele homestead, built in 1837-8. In 1835 Mr. Tonnele bought the old Dr. Hornblower place, on the west side of Summit avenue, a ten-acre plot, extending from a little south of what is now Magnolia avenue to the center of what is now Pavonia avenue, where it joined a Van Reypen farm. Dr. Hornblower served in the Revolution, having joined the army from Belleville. After the war he studied medicine, and came to this locality in 1789, and began the practice of medicine—the first doctor known to have practiced in Jersey City. He married, and built a house about the[Pg 142] center of the block between Pavonia and Magnolia avenues. The date of building is not known, but probably it was about the beginning of the century. The house had a wing on either side—one used as an office, and the other as a kitchen. After Mr. Tonnele bought the property he removed the main part of the house to its present location on the southwest corner of Magnolia and Summit avenues, leaving the wings for a lodge and gardener's cottage. Along Summit avenue he built a high stone wall with iron gates, about where the old house had been. Inside the wall was a hawthorn hedge and a row of mulberry trees. A driveway, bordered with cherry trees, extended from the gate and around a circular lawn in front of the house, which stood on the west side of the grounds. It was built of trap rock, some forty feet square, three stories and basement, with a wide veranda in front. A wide central hall with large rooms on either side. The ceilings were beautifully frescoed, the mantels were of Sienna marble, and the doors of solid mahogany. It also was heated from a great stove in the hall and grates in the rooms. It is said that John Kelly, the Tammany Sachem of New York, put the grates in the house. The grounds were beautifully laid out, and many of the fruit trees were imported from France. The furniture for the house was made by a Frenchman in New York.
Mr. Tonnele was born in New York City; his mother a daughter of General Waterbury, of Connecticut, and his father a Frenchman, who came to this country about the time of the Revolution. He founded a chamois glove factory in Water street. It is said that[Pg 143] he never spoke a word of English, nor did his wife ever speak a word of French. Mr. Tonnele, of Jersey City, was the first Catholic member of the New Jersey Legislature, and served in county offices. He laid the corner stone of the Court House. The old stone house has passed through numerous changes in its comparatively short life. From the hospitable home of the Tonneles it became the first home of Christ Hospital, later a tenement house. The grounds have been sold off in city lots, and the old walls are a dilapidated ruin.
The question is often asked, what is there and what can there be in Jersey City? It is a question that cannot be briefly answered; this book only answers it in part. We have very much that should make us proud of our city. Our location is superb, our historic legacies are rich and enviable. But few American cities can boast of church and school in uninterrupted continuance for two hundred and thirty-eight years. There might be given a long list of names of citizens, honorable and upright men, whose lives in many ways reflect glory upon their city; business men, patriots, clergymen, lawyers and judges, who have made Jersey law a synonym for justice and right; doctors whose lives have been a constant blessing to the sick and suffering; men in all walks of life, whose simple devotion to duty has made the world better. Phillips Brooks said that "no man, woman or child could think a good thought without the world being better for it."
Of course, there are shadows, but, if we choose, they can easily be removed. Our streets are not as clean[Pg 144] as we hope they soon will be, but it is claimed by good authority that there is less crime here than in any other city of its size in the world; and city streets are more easily made clean than criminal characters reformed. Let our citizens once realize that our city will become just what we choose to make it, and its future is assured—a future of honor, of beauty, of substantial, thorough excellence in all directions. The foundations are already laid.
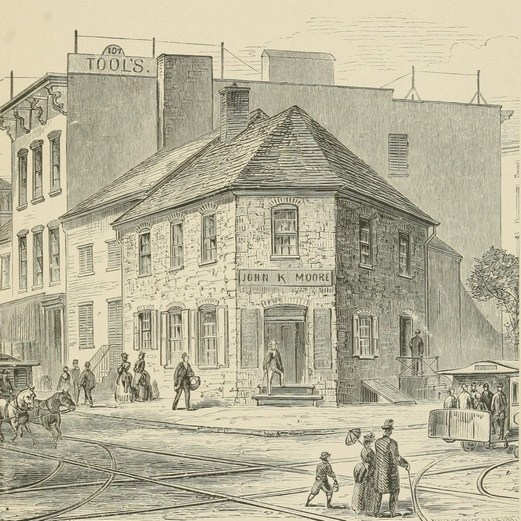

The Old Stone House.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of Jersey City and its Historic Sites, by
Harriet Phillips Eaton
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK JERSEY CITY AND ITS HISTORIC SITES ***
***** This file should be named 47936-h.htm or 47936-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.org/4/7/9/3/47936/
Produced by Alan and the Online Distributed Proofreading
Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was produced from
images generously made available by The Internet Archive)
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.org/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.org/license
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.org),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH 1.F.3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, are critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including checks, online payments and credit card donations.
To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.org
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.